Coronavirus hit this rural Kansas area late and hard. But don’t look for residents in masks

As communities in rural northwestern Kansas endured some of the state’s biggest spikes in coronavirus cases last week, a county sheriff who was among those testing positive found himself struggling to breathe and landed in a hospital room more than an hour from home.
The COVID-19 pandemic arrived late in this corner of the U.S., but it’s now putting Kansas’ Gove County under considerable stress. The county has had to send patients, including Sheriff Allan Weber, to hospitals in other towns, and its 22-bed medical center has only a handful of beds dedicated to COVID-19 cases and not enough staff to monitor the most serious ones around the clock.
Most of the 30-plus residents in the local nursing home tested positive, and six have died since late September. Besides the sheriff, the county’s emergency management director, the hospital’s CEO and more than 50 medical staff have also tested positive.
Even so, some leaders are reluctant to stir up ill will by talking about how often friends and neighbors wear masks, or questioning how officials have responded.
“The hospital has a sales tax initiative that’s on the ballot, and we just don’t want to upset anybody,” said David Caudill, CEO of the Gove County Medical Center, who tested positive for the virus. The medical center includes the community hospital and the nursing home.
Gove County is perhaps best known for an isolated stand of chalk pyramids that can tower 60 feet above the prairie, and some of its 2,600 residents live closer to Denver than to Kansas’ capital, Topeka.
The 51-year-old nurse worked more than two decades at the same medical center in Apple Valley where she fell ill and ultimately died.
President Trump is popular here, and local officials quickly ditched a mask mandate this summer after getting heat from some residents amid the president’s criticism of such policies. Funerals and weddings went ahead. So did a homecoming football game between its two high schools on the last Friday in September, although people were encouraged to wear masks.
The sheriff, who has since been released from the hospital, was fielding calls last week from the Hays Medical Center. A pulse oximeter began beeping, indicating that his oxygen levels were low. He coughed and took deep breaths.
“It’ll quit here in a minute,” he said.
Weber has been hospitalized in the past for asthma attacks, but the coronavirus symptoms were more pronounced. “You got body aches and headaches. The tightness in my chest is different.”
If you were counting on a coronavirus infection to keep you safe from COVID-19 without having to get a vaccine, scientists have some bad news: It won’t work.
The state health department said coronavirus cases in Gove County doubled during the two weeks ending Wednesday, from 37 to 75, and that the spike was proportionally among the largest in Kansas. Local officials and doctors say the real number was even higher: 140, with 88 in the past two weeks and almost all of them since Sept. 1. There have been seven coronavirus-related deaths — again, proportionally among the highest in the state.
“We have community spread to the point that we have not been able to pin down the root cause of any of our cases for the past month,” said Dr. Scott Rempel, the county’s health officer, one of five physicians in Gove County.
The county commission imposed a mask mandate starting Aug. 6, when only a handful of cases had been reported, but repealed it 11 days later. Rempel said it was “heartbreaking, from a public health perspective.”
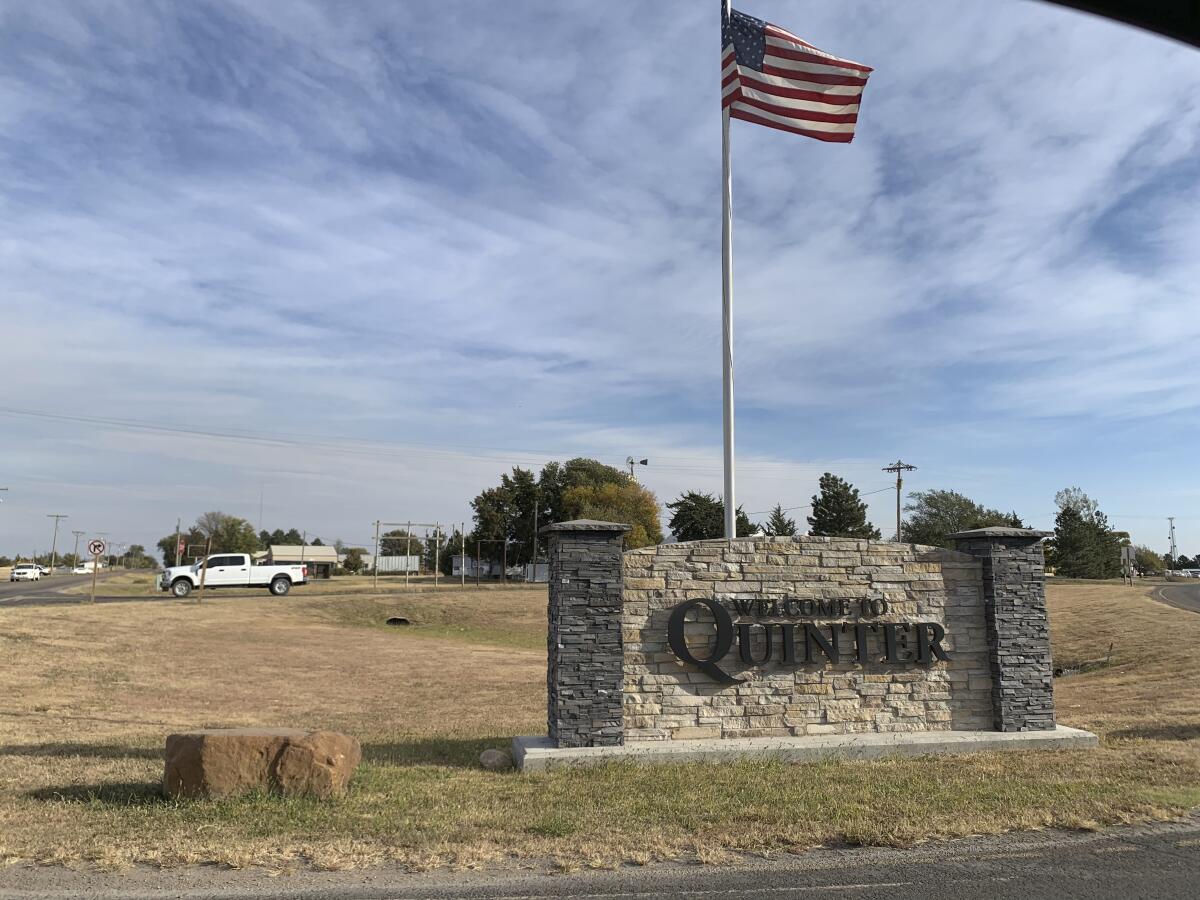
In Quinter, the county’s largest town, with about 1,000 residents, public schools are holding in-person classes and requiring the 300 students and staff to wear masks. Students eat their lunches outdoors under tents, and the district has bought heaters and plans to use its bus barn if the winter weather gets too cold.
Superintendent Kurt Brown is careful to avoid the political debate about masks or to comment on rules elsewhere in the state.
“Every conversation surrounding this is a difficult conversation,” Brown said.
Gary Kraus, the superintendent in the neighboring Grainfield and Wheatland school districts, said classes are small enough to accommodate social distancing with some changes in scheduling for the high school. He said the districts thought about imposing mask requirements as school was preparing to start, but “I didn’t want to fight that political battle” because “it’s so stressful and time-consuming.”
With officials’ response to COVID-19 politicized in an election year, Kansas’ Democratic governor and the Republican-controlled Legislature have been at odds for months. More than two-thirds of Gove County’s voters are registered Republicans, and Trump carried the county with nearly 85% of the vote in 2016.
In Grainfield, home to about 240 people, Terry Cox doesn’t wear a mask in his farm supply store, nor do most of his customers. Now that it’s so close to home, he sees the coronavirus as no worse than “the regular flu.” His store’s bookkeeper and his sister-in-law have tested positive, and his brother, who lives two counties away, was hospitalized. Cox wears a mask when shopping in Quinter, though.
Quinter resident Judy Wolf, a cook at a senior center, said media outlets reporting on the pandemic need to “quit making a mountain out of a molehill.”
“Everybody’s going to get it and go on with your lives,” she said. “The only ones that are dying are the ones with other health issues.”
Deaths from COVID-19 in the U.S. reach 200,000 as authorities across the country continue to struggle to curb its spread.
Doug Gruenbacher, another Gove County doctor, contracted the coronavirus in September and recovered along with his physician wife, Shelly. He said county residents have concerns about personal liberties and “not wanting to be told what to do.”
“That’s part of the reason of why we love it here, because of that spirit and because of that independence,” he said. “But unfortunately, it’s something that also contributes to some of the difficulties that we’re having right now.”
More to Read
Start your day right
Sign up for Essential California for news, features and recommendations from the L.A. Times and beyond in your inbox six days a week.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.