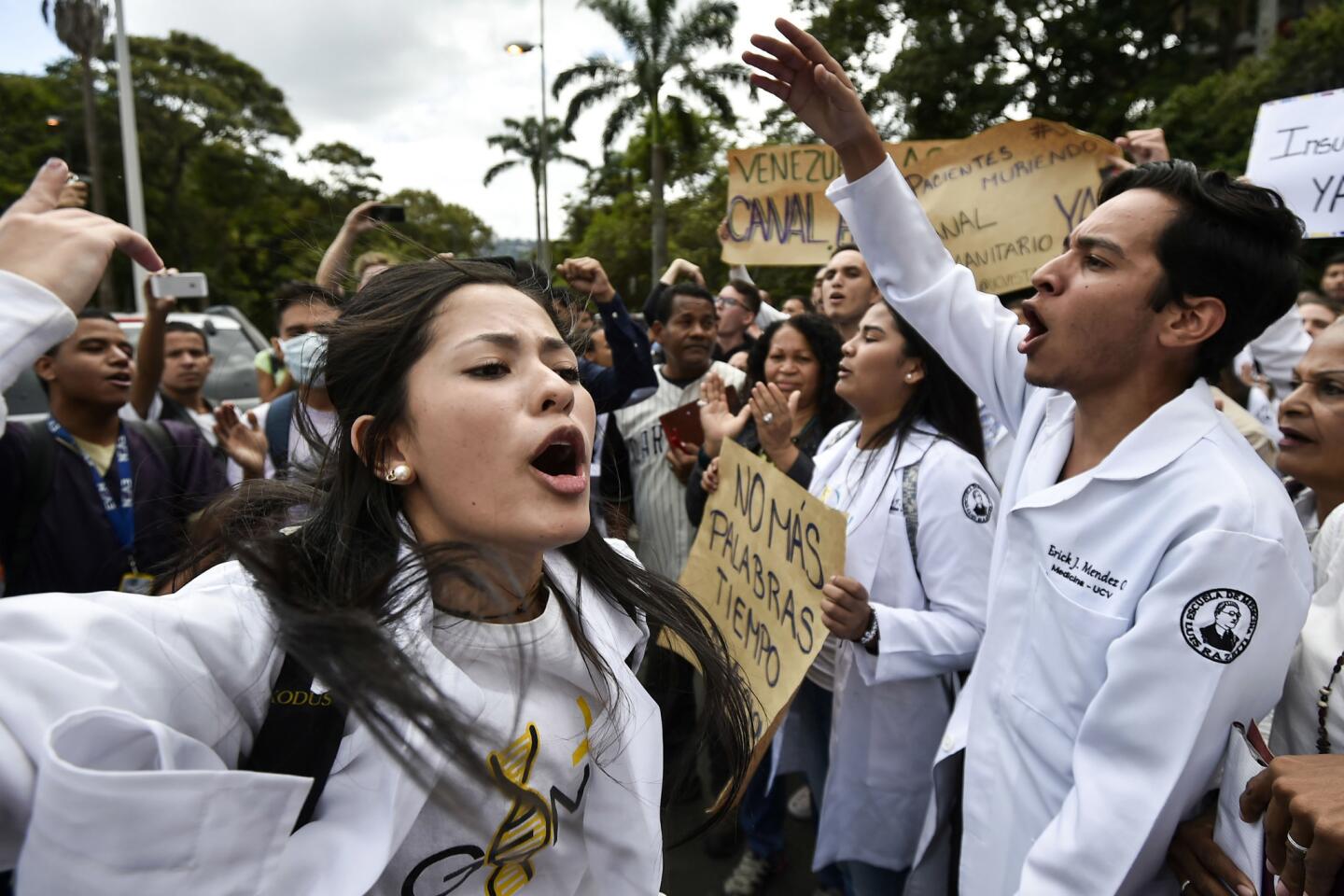Trump recognizes Juan Guaido, head of Venezuela’s opposition, as country’s interim president
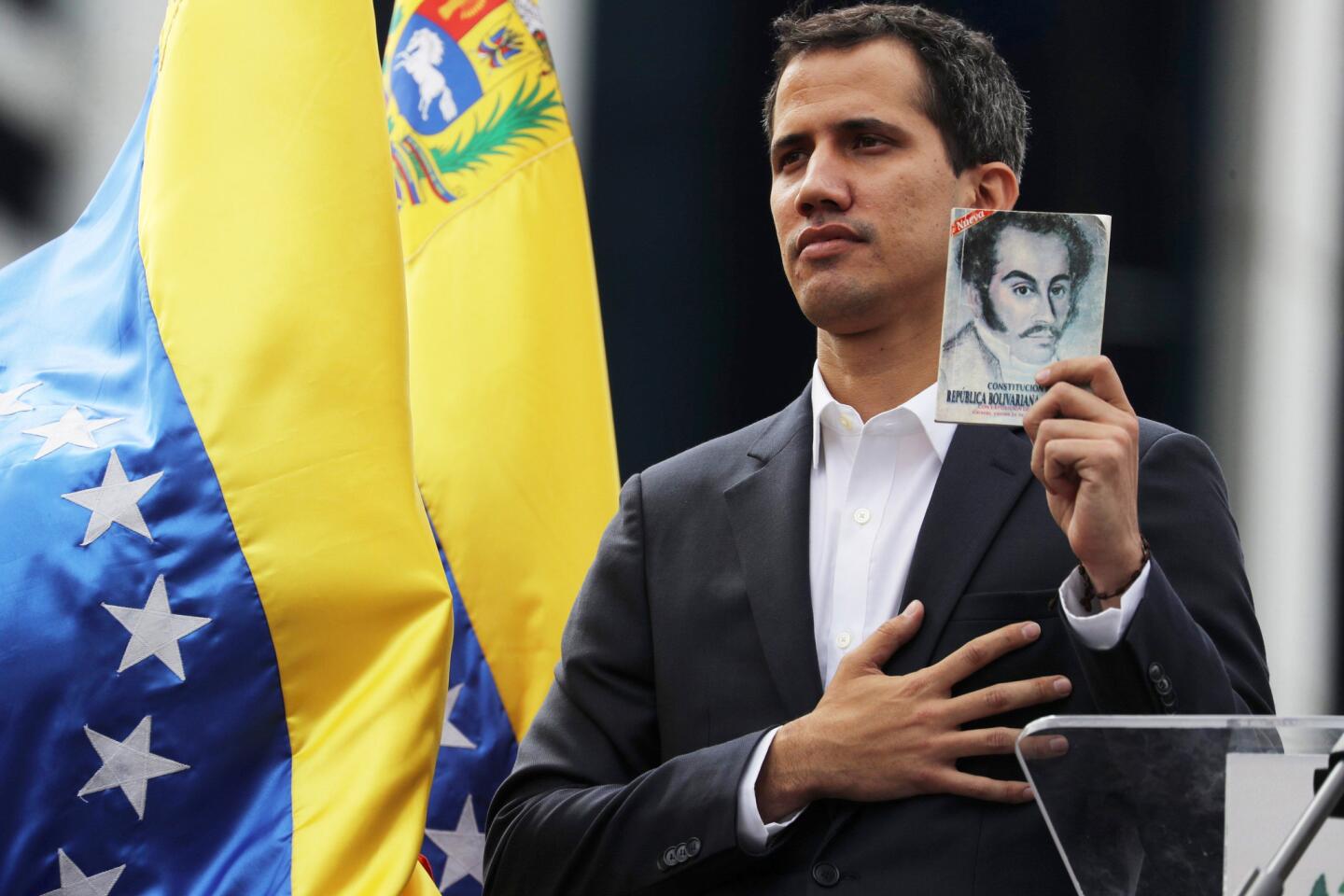
U.S. President Donald Trump recognized the president of Venezuela’s opposition-led National Assembly Juan Guaido as the interim president of the crisis-mired South American country on Wednesday.
The parliament is not expected to convene until Thursday at the earliest. Guaido declared himself interim president on Wednesday.The Trump administration has been inching toward such a declaration ever since Nicolas Maduro was inaugurated earlier this month.
Maduro was re-elected last year but the opposition in the country says the election was fraudulent and does not recognize him.Recognition of Guaido by the U.S. increases international pressure on Maduro to step down and could result in severe economic consequences for his government amid an already painful economic crisis in the once-prosperous oil-producing nation.
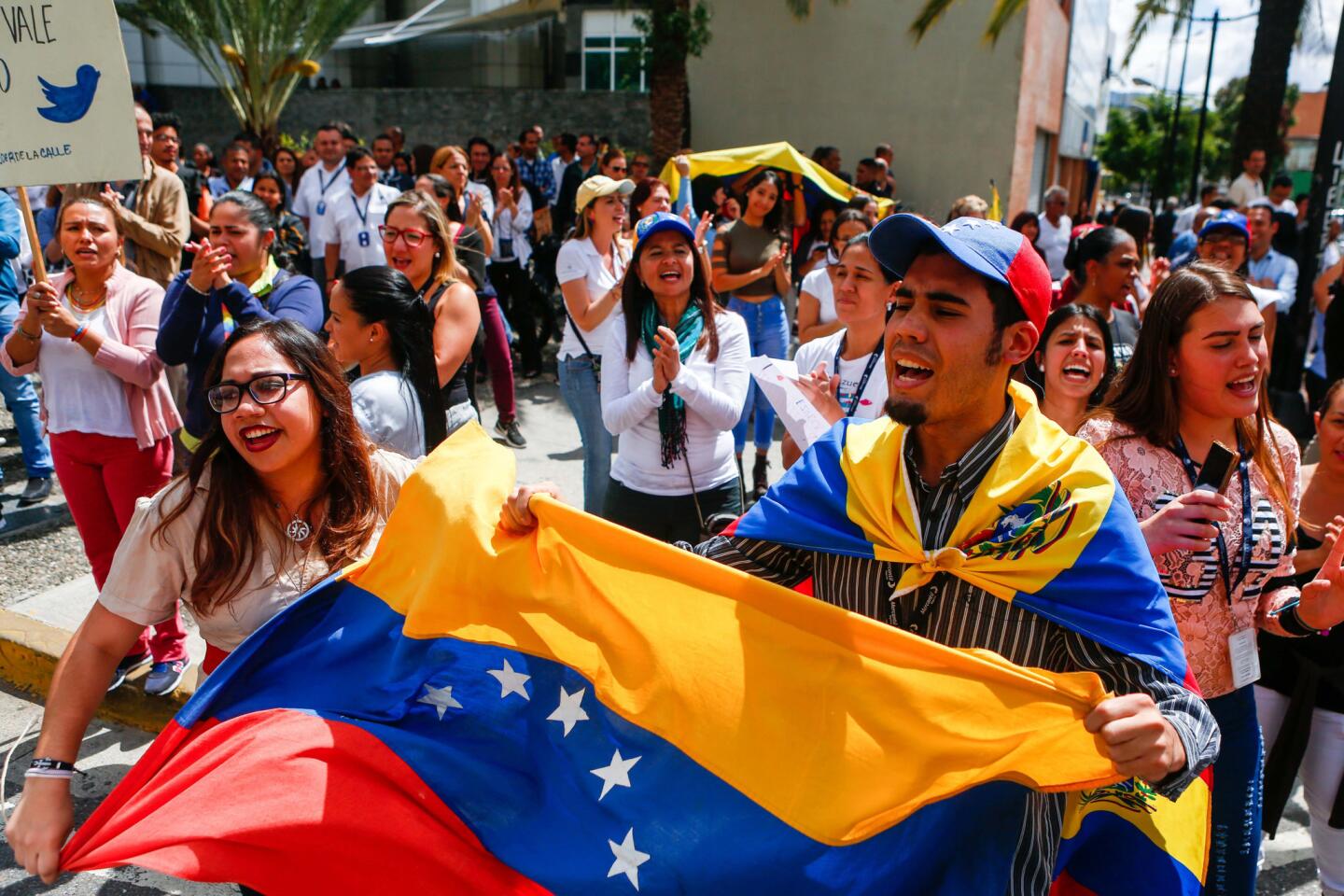
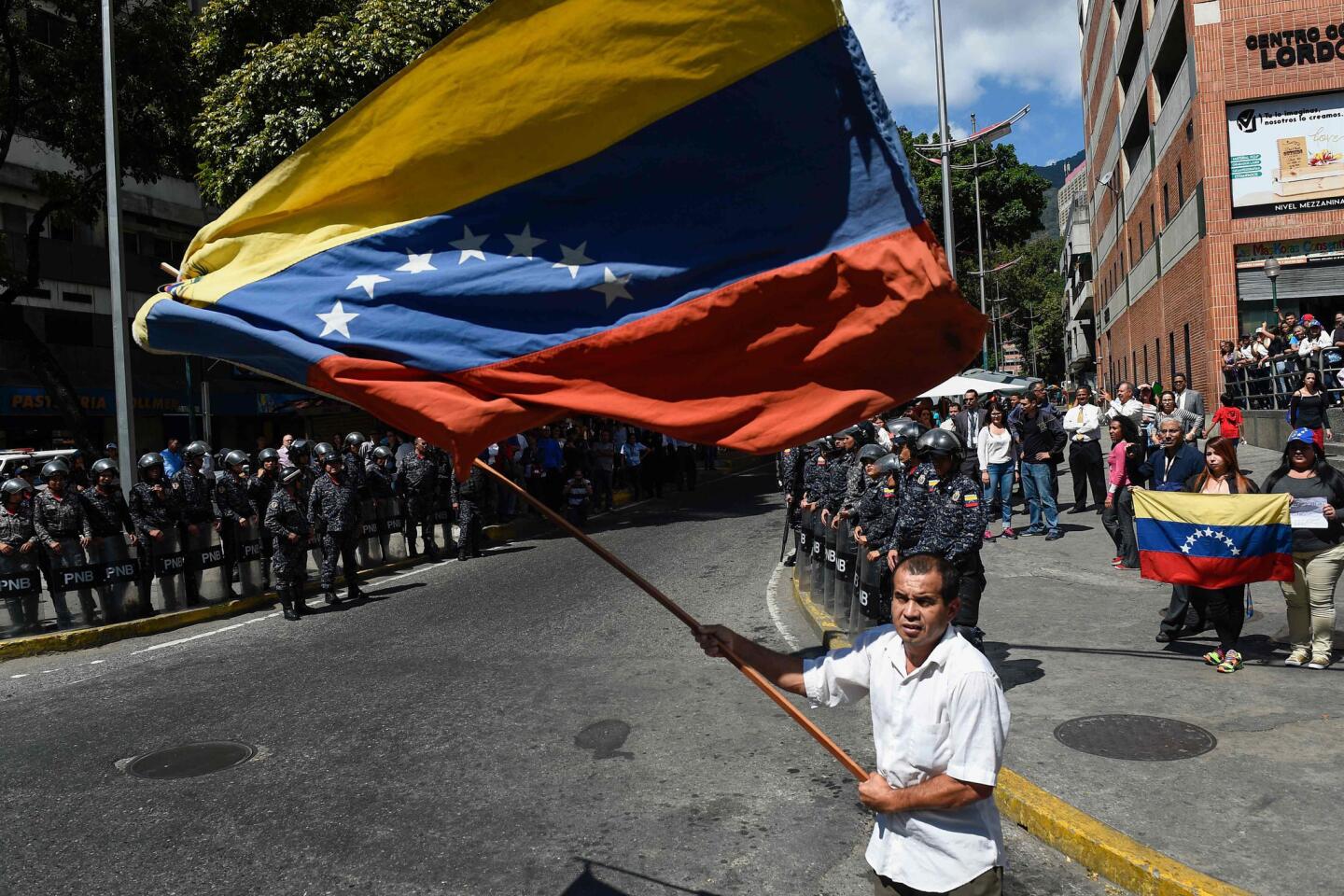
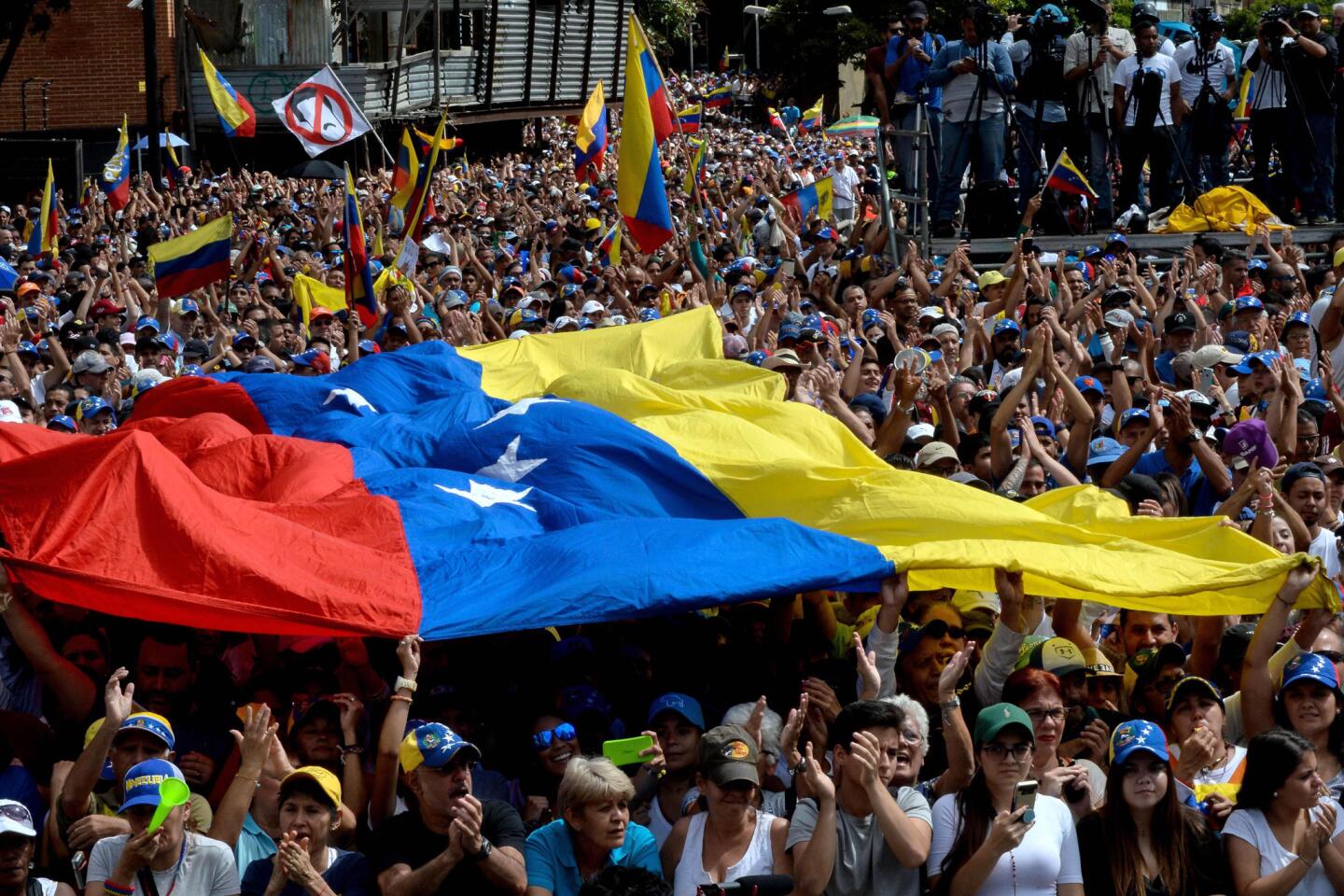
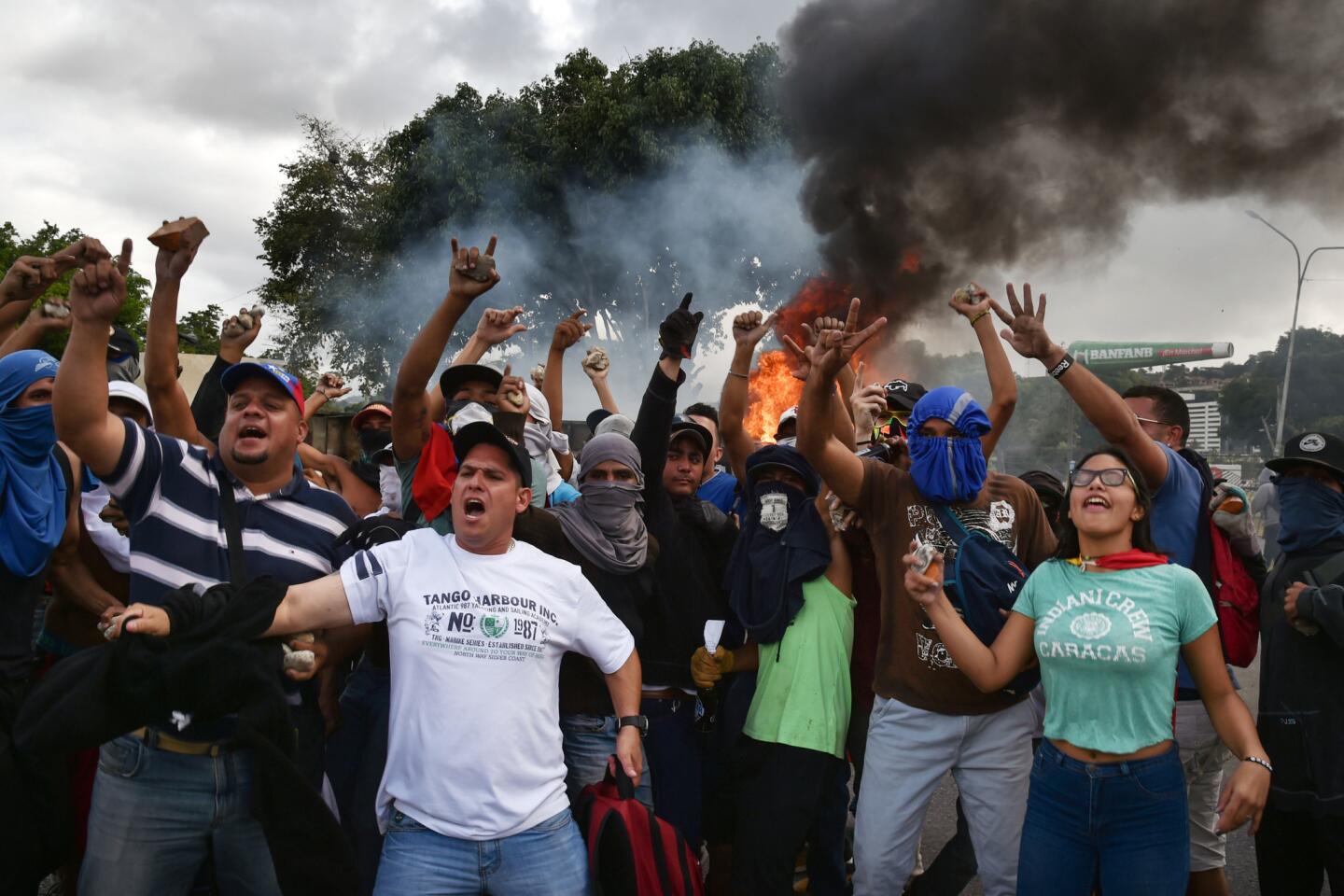
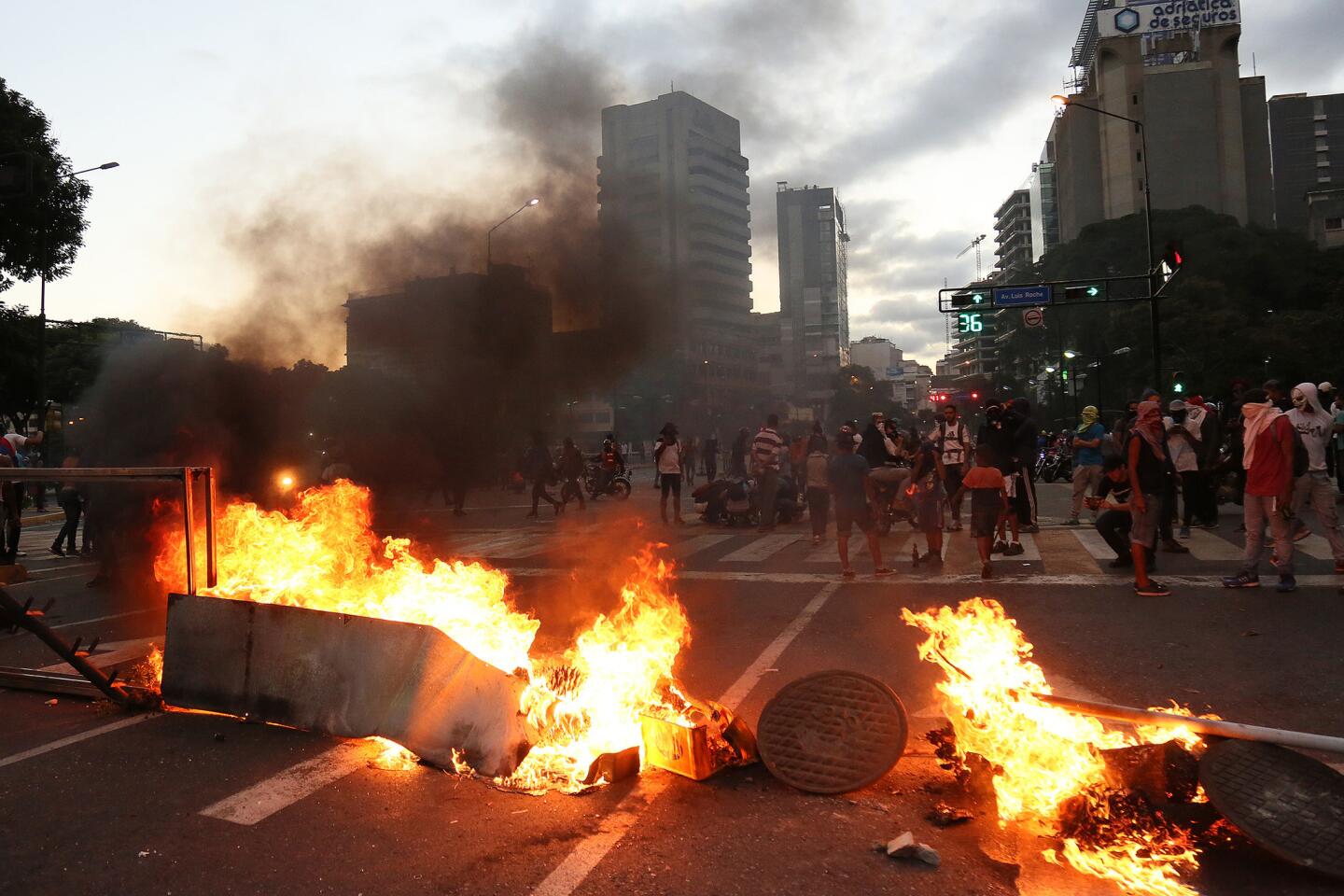
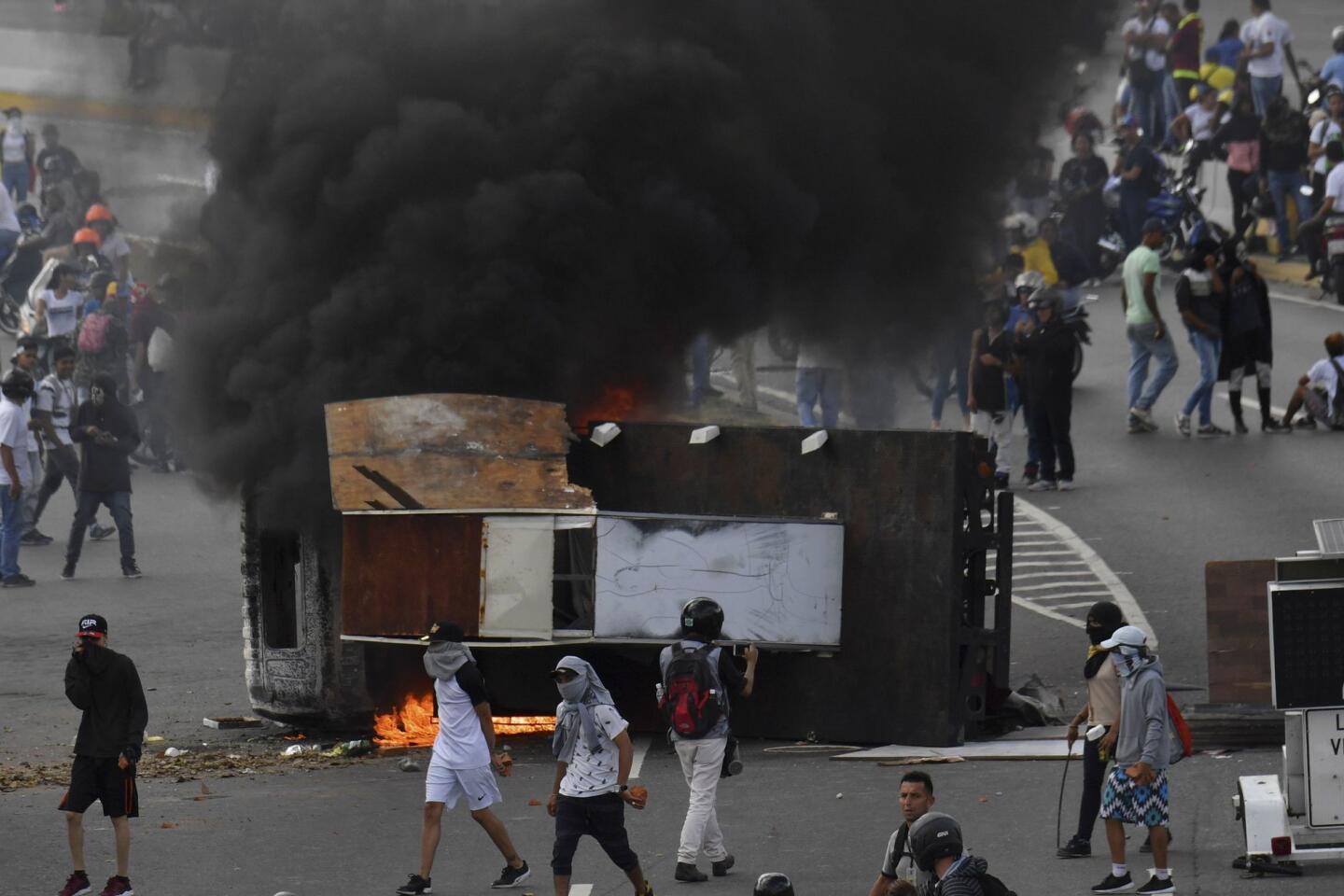
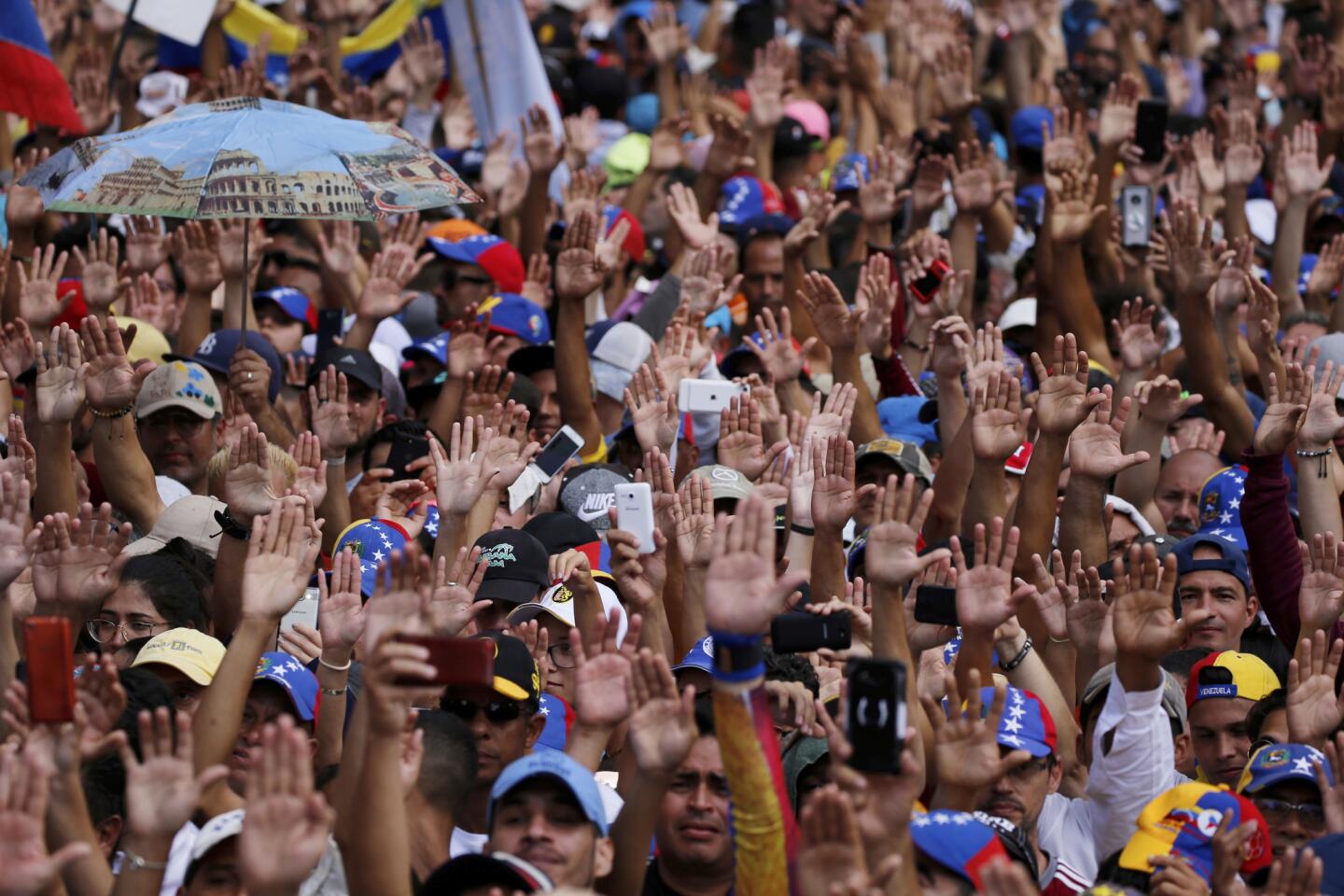
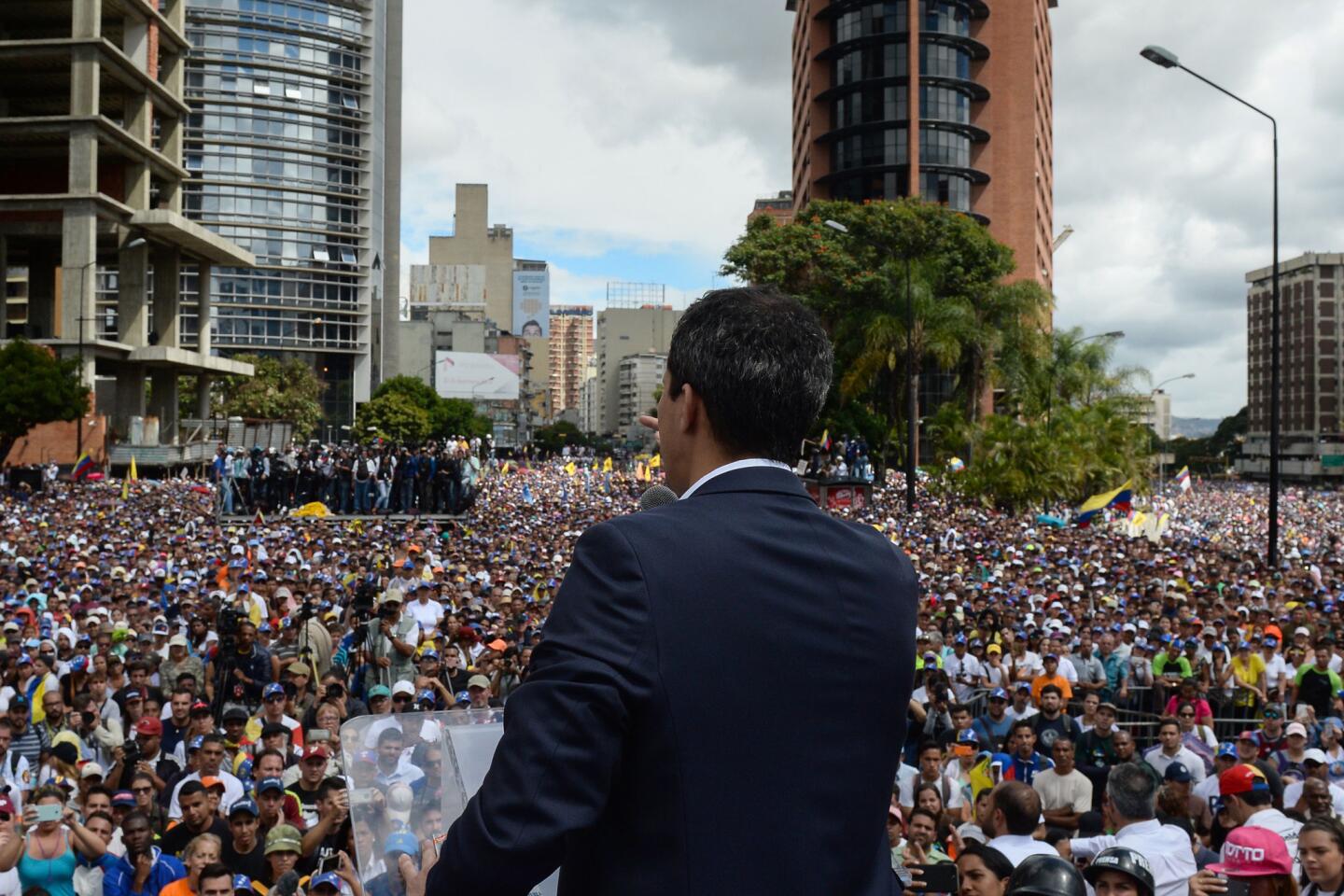
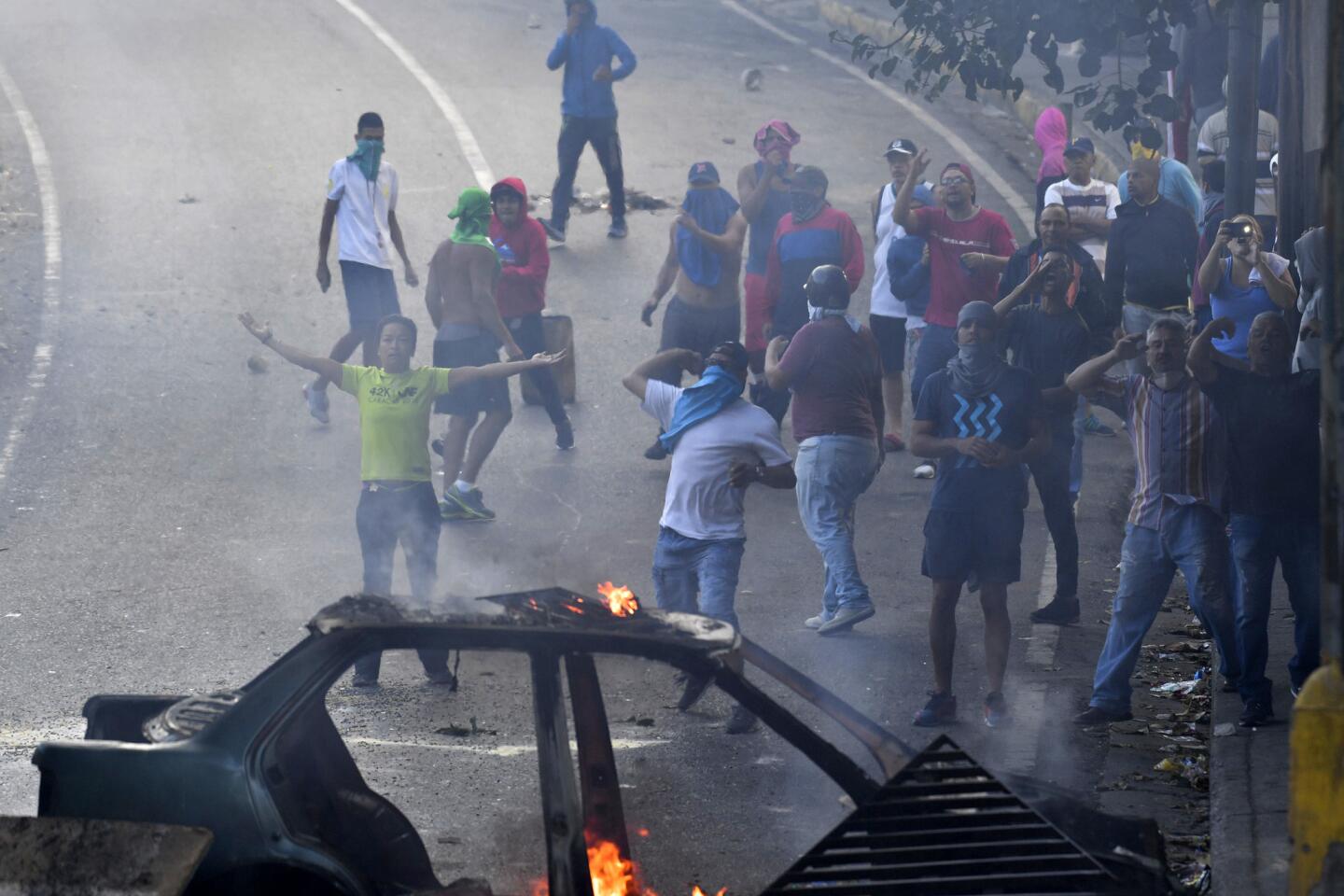
Thousands of Venezuelans filled the streets Wednesday accusing embattled Maduro of usurping power, and joining the nation’s reinvigorated opposition movement in demanding he step down as the country reels from a crushing economic crisis that has forced millions to flee or go hungry.
Large crowds of protesters gathered in Caracas waving flags and chanting “Get out Maduro!” in what was shaping up to be the largest demonstration since a wave of unrest that left more than 120 dead in 2017.
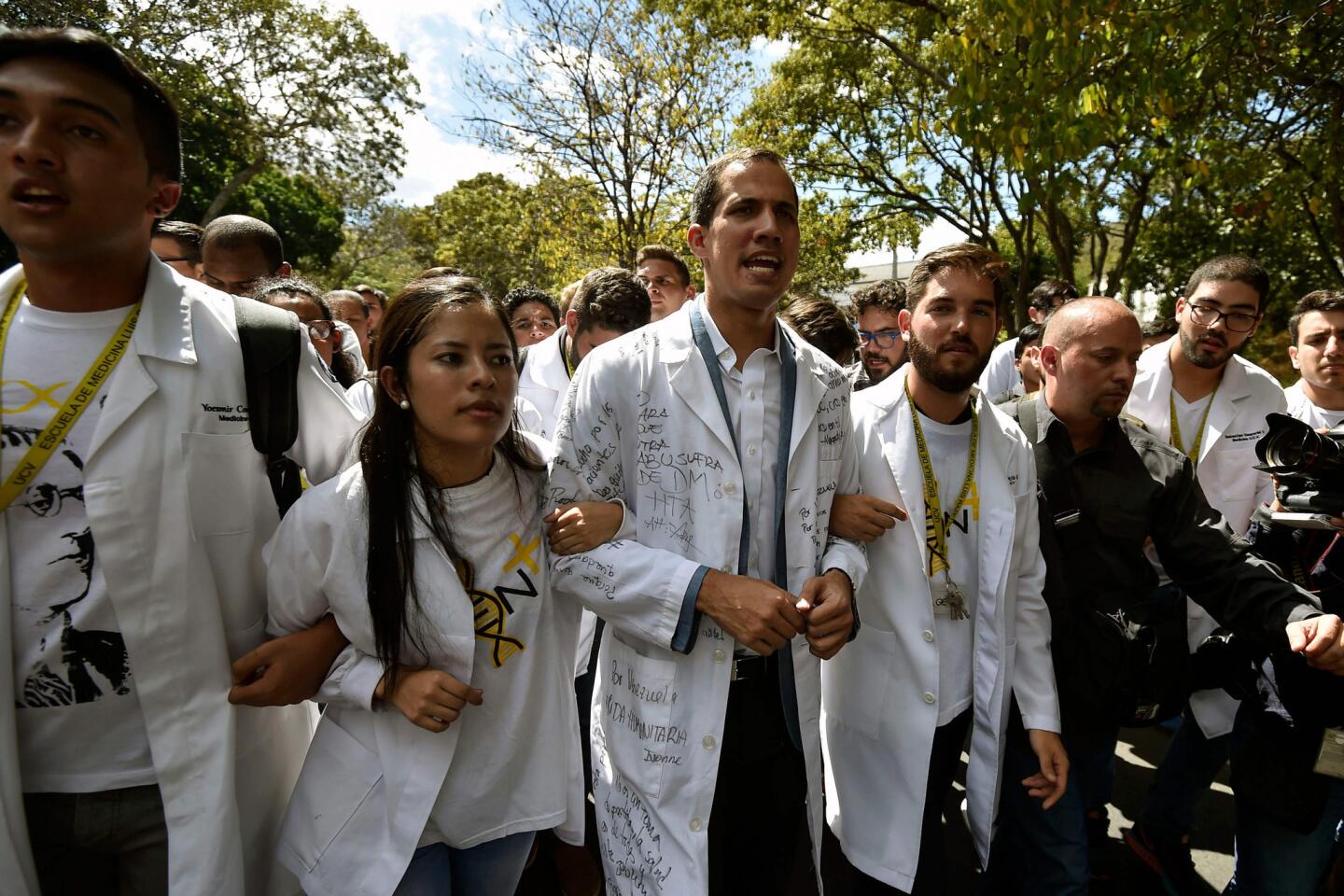
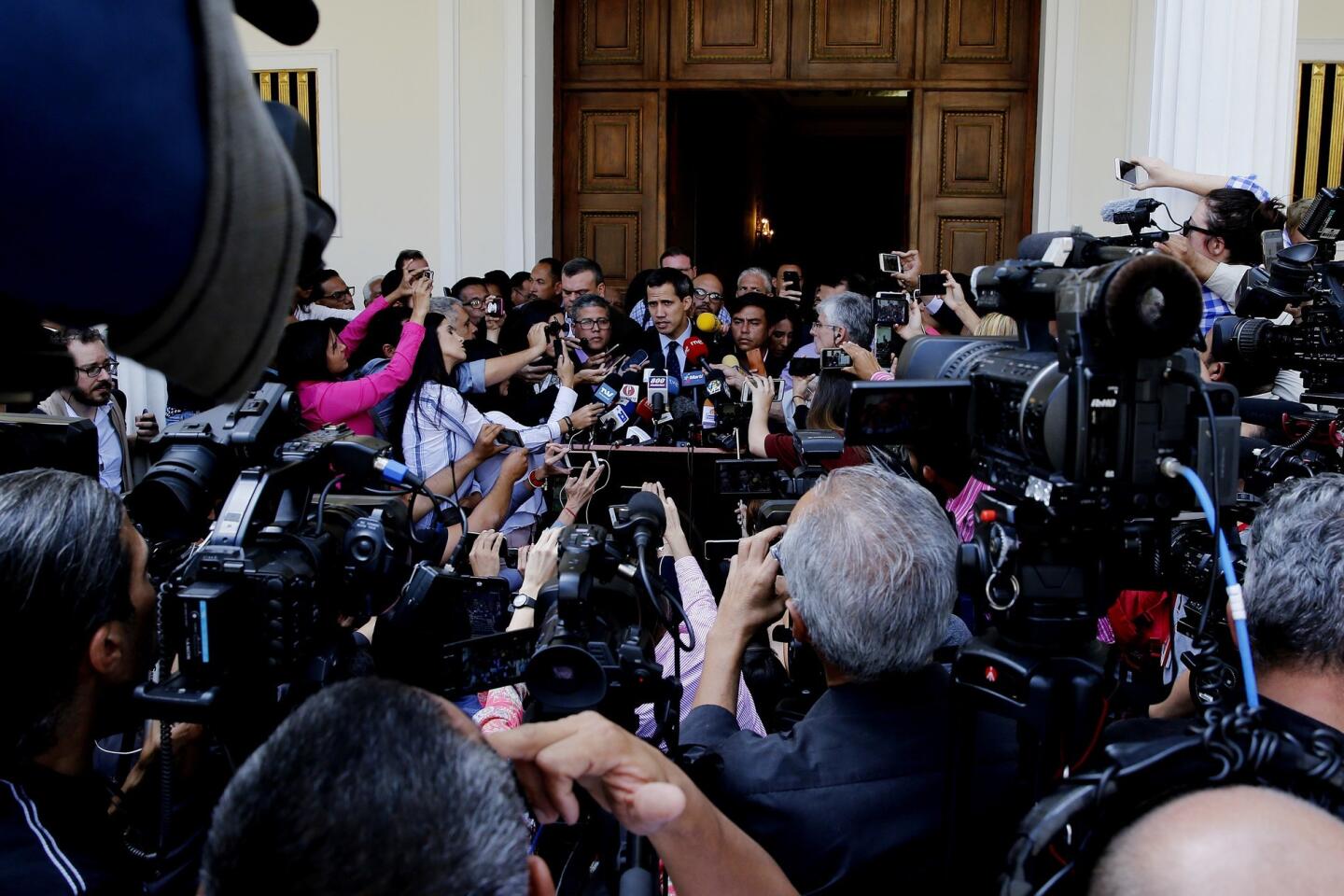
“Venezuela is reborn on the streets today, searching for freedom and democracy,” Juan Guaido, the 35-year-old opposition leader who has sprung into the limelight since taking the helm of the opposition-controlled National Assembly, declared on Twitter.
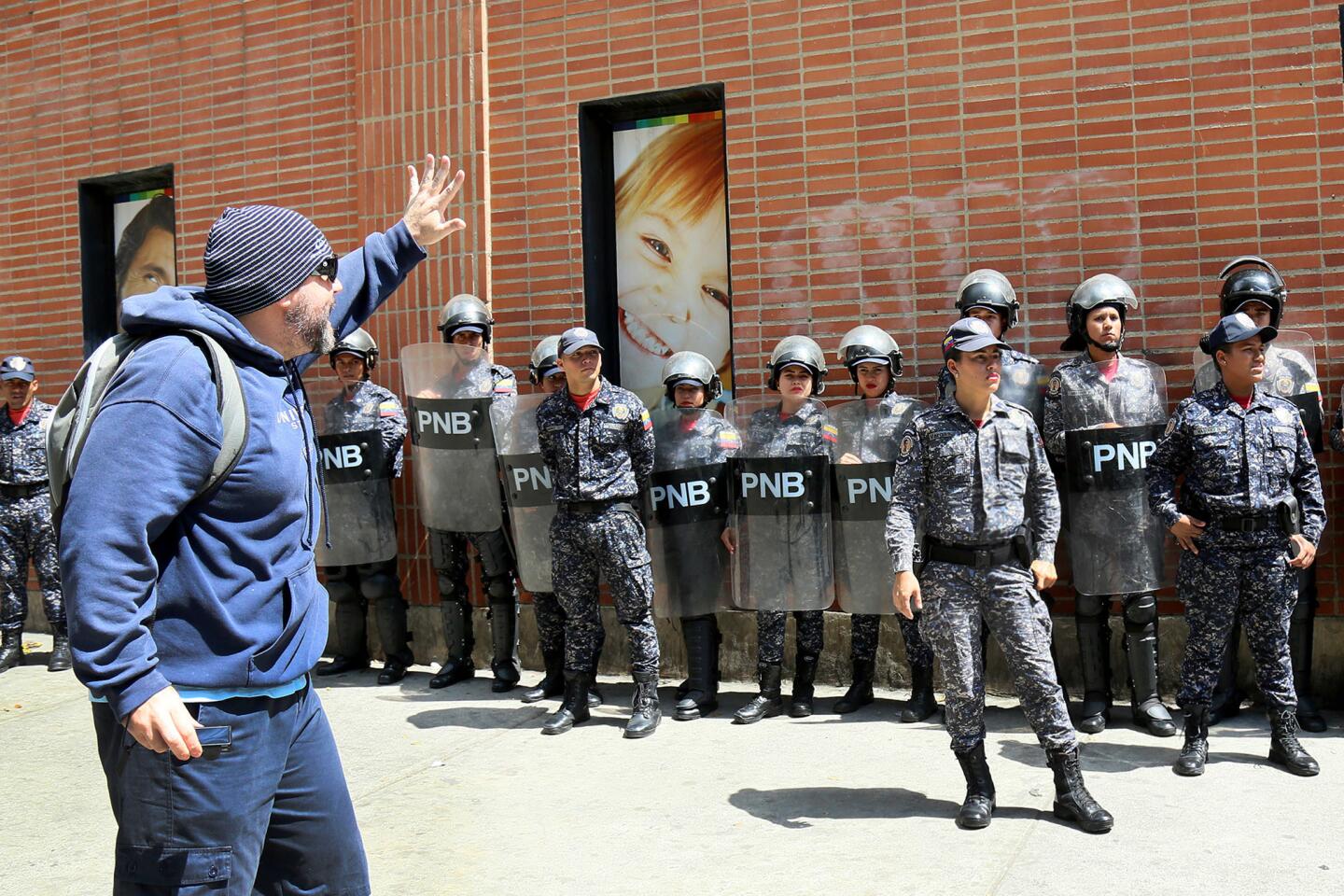
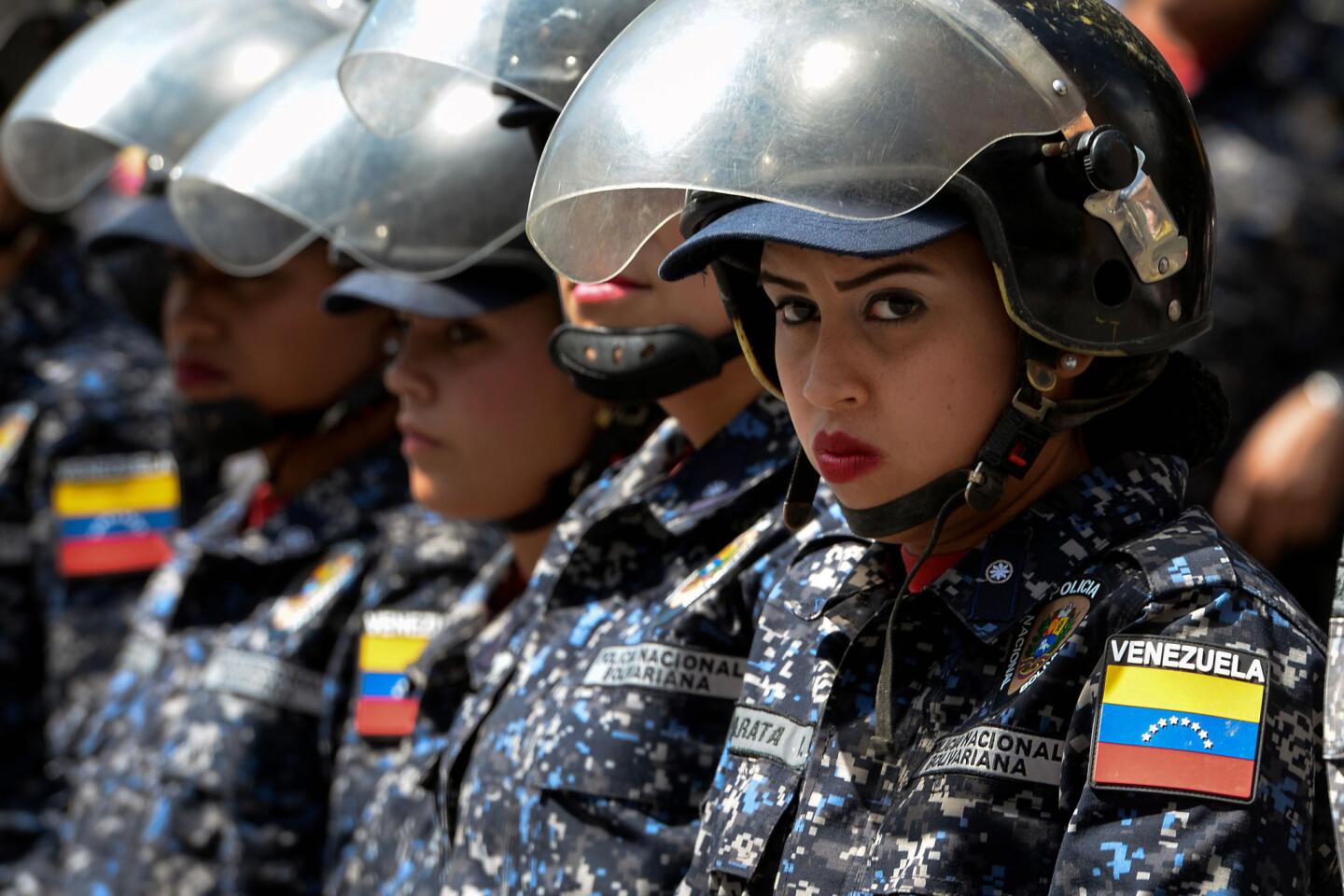
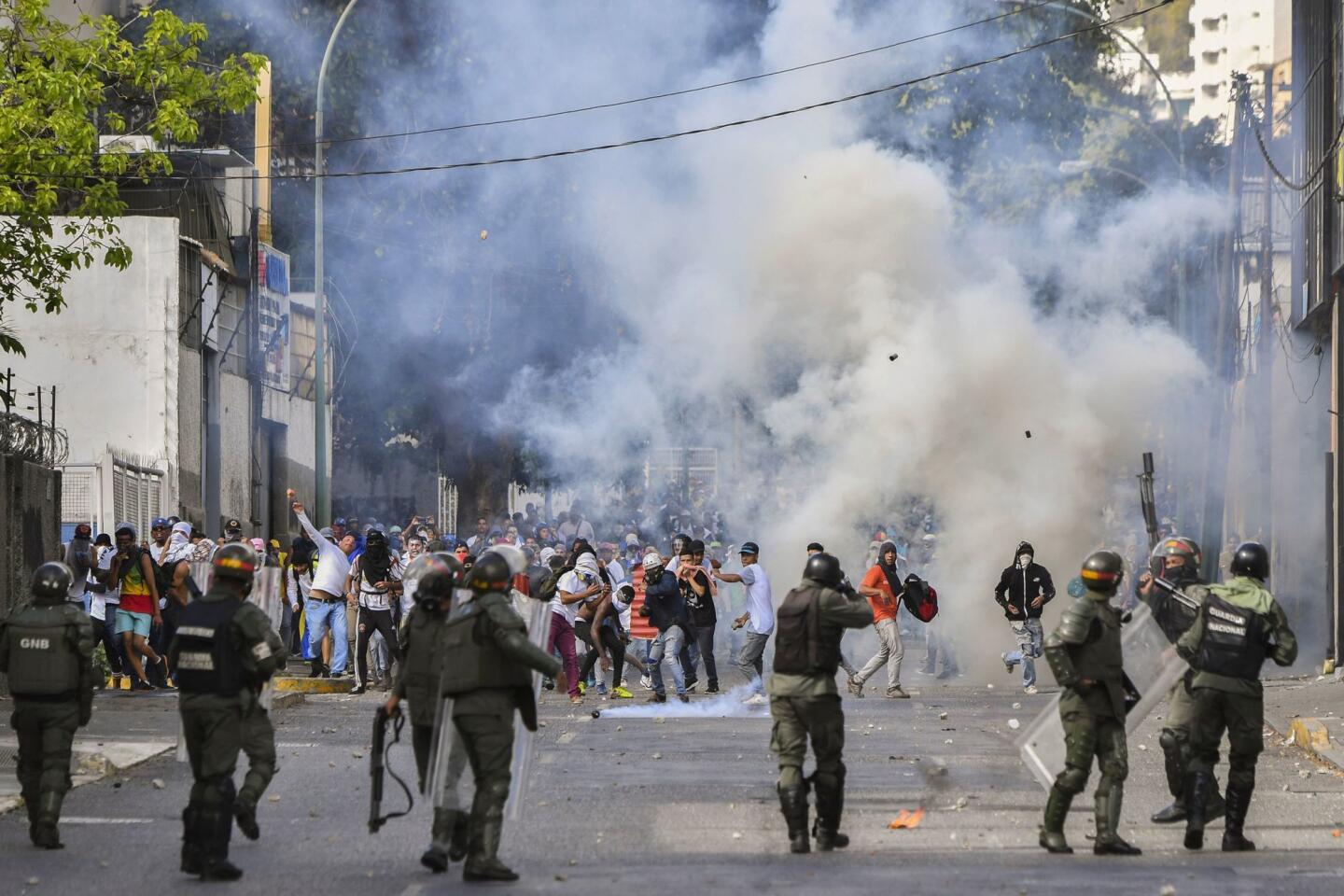
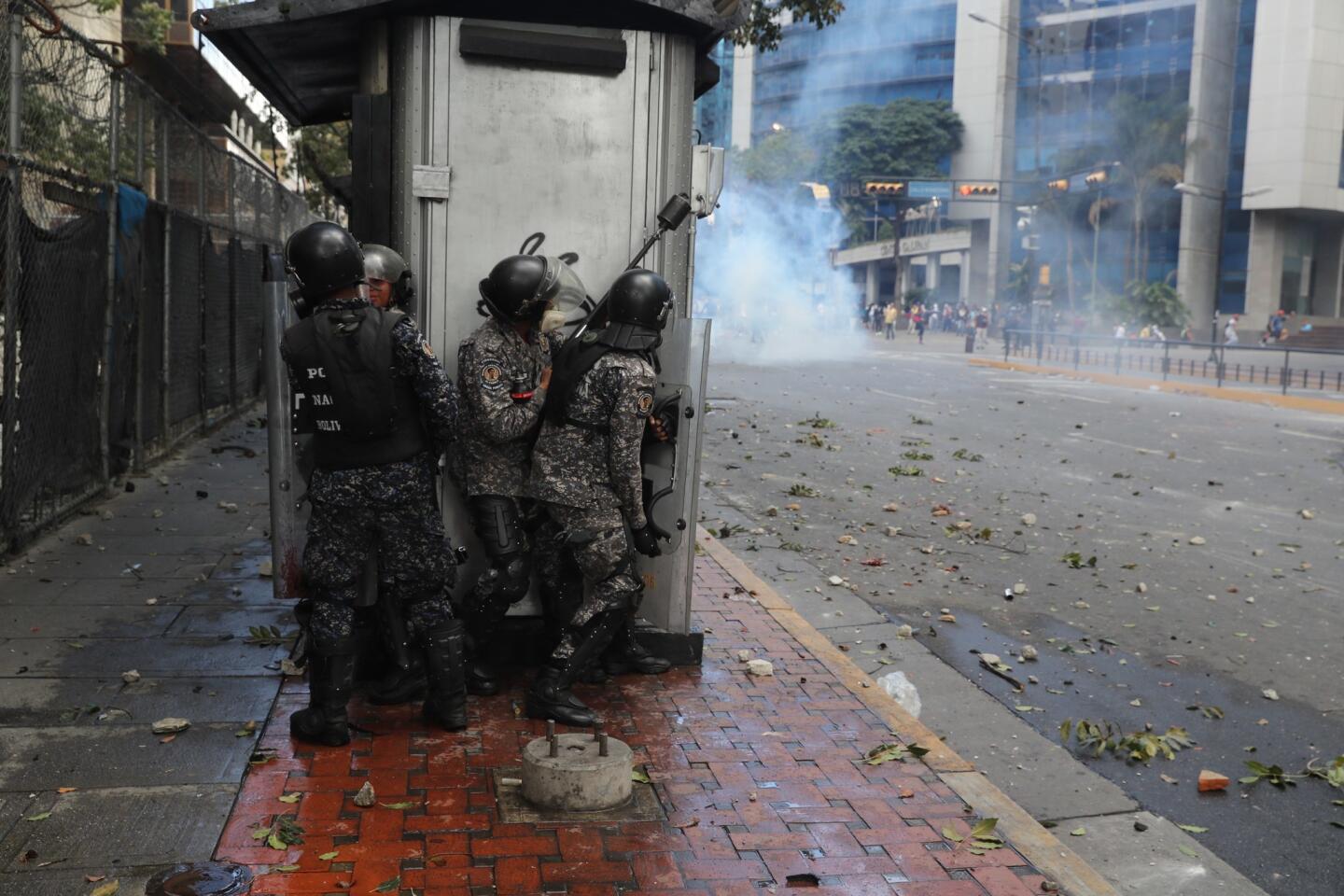
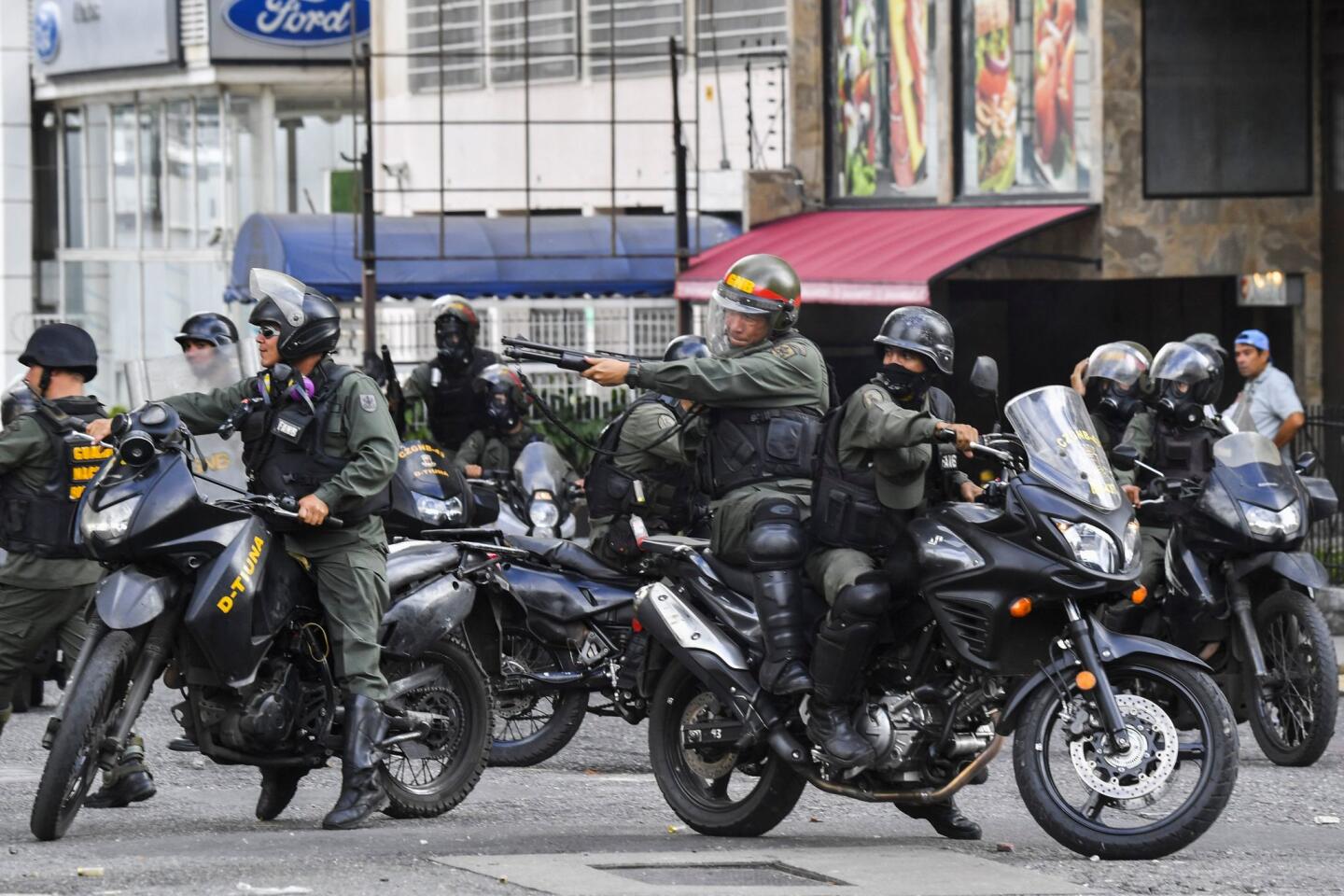
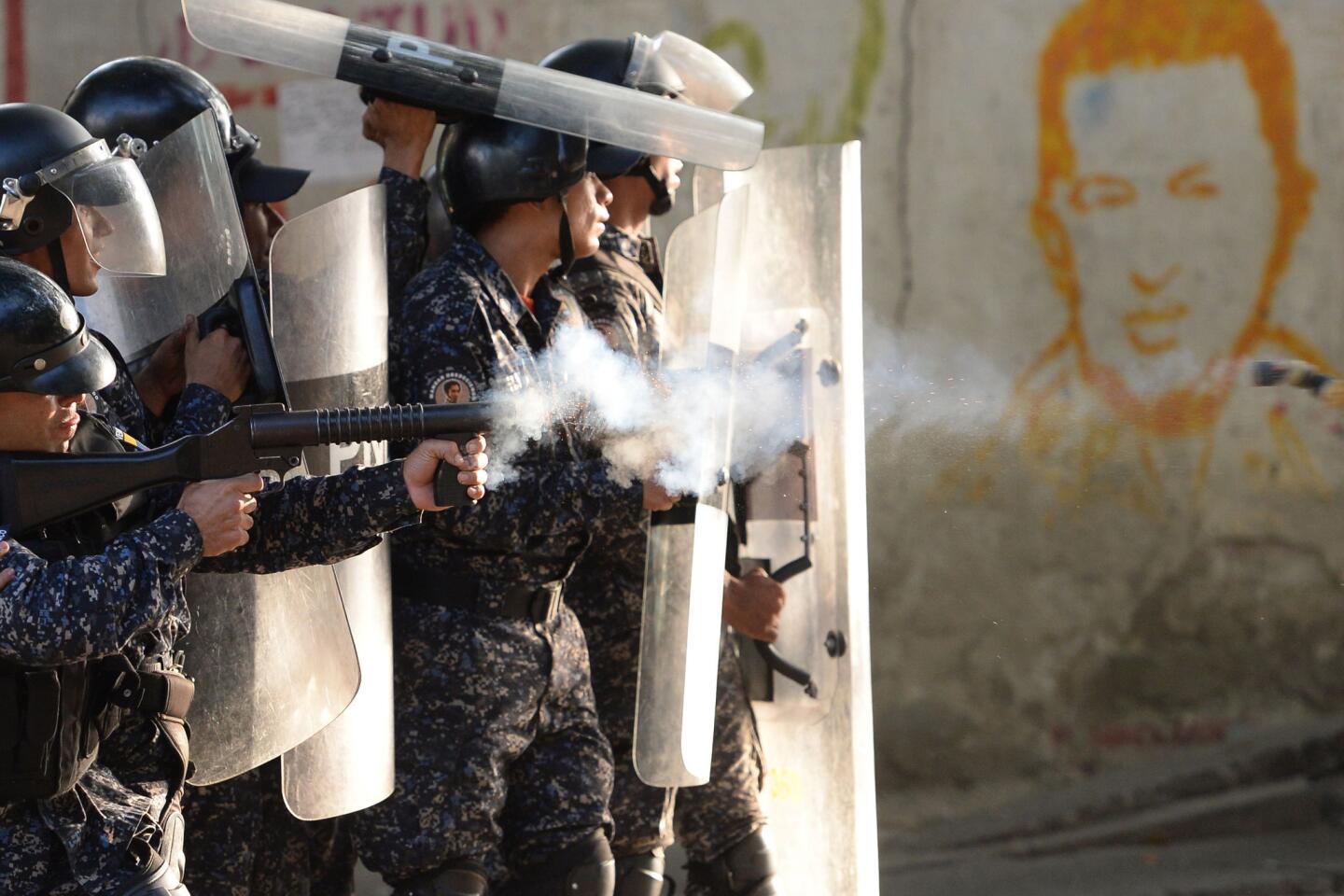
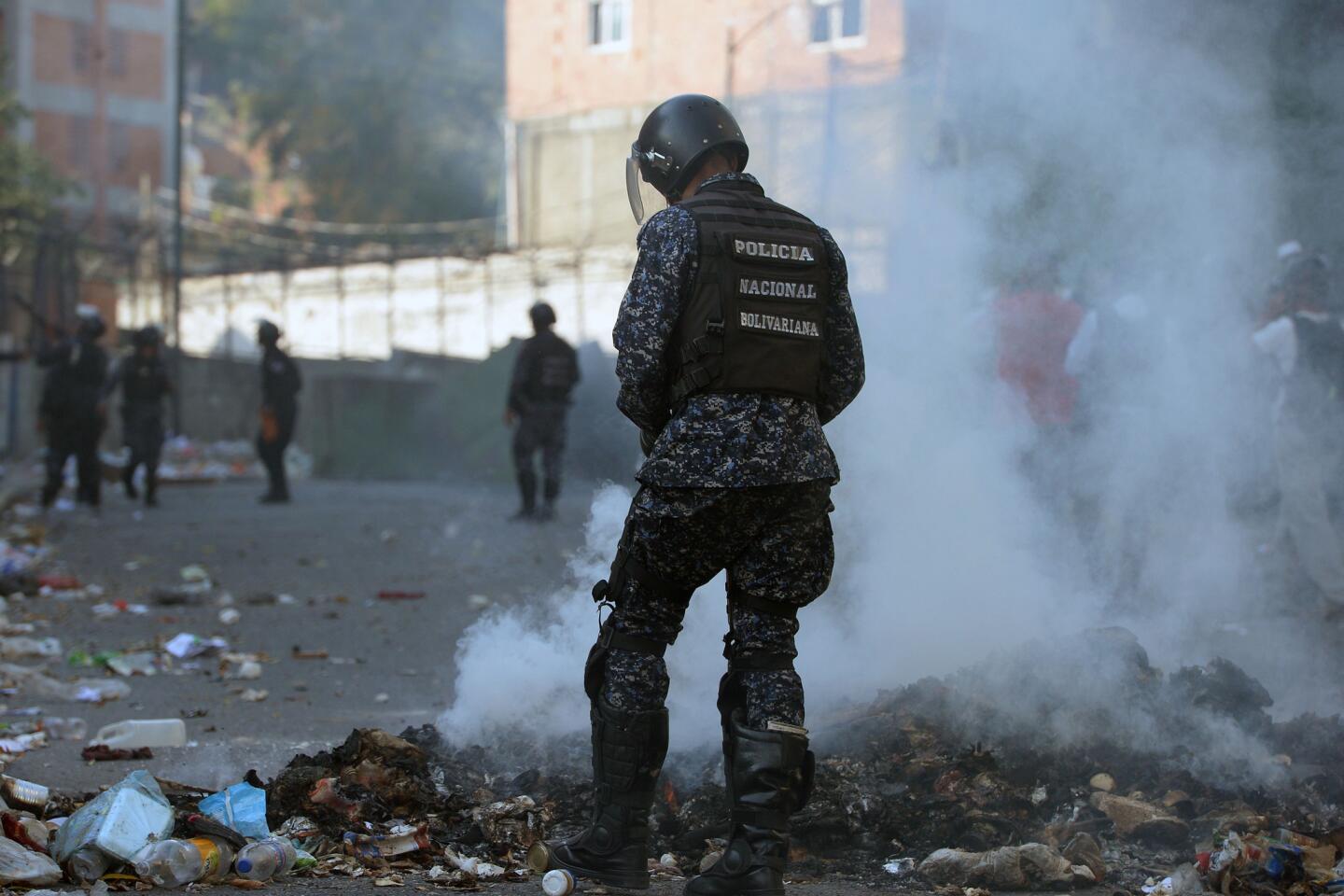
Pro-government demonstrators dressed in red in support of Maduro were also marching in the capital, at times crossing paths with opposition protesters and shouting “sellouts” and “traitors.” National guardsmen launched tear gas at anti-government protesters in the middle-class neighborhood of El Paraiso, but for the most part, the marches continued without conflict.
“Join us!” the protesters cried out to a line of officers wearing helmets and carrying shields. “You are also living this crisis!”
The protest is considered a crucial test for the opposition as it seeks to send a forceful message that Maduro no longer has the people’s backing, and appeals to the military and the poor to shift loyalties that until recently looked solidly behind the president. The protests were called to coincide with a historic date for Venezuelans — the anniversary of the 1958 coup that overthrew military dictator Marcos Perez Jimenez.
“The democratic forces are here advancing,” opposition leader Maria Corina Machado said as she marched. “Not so that Maduro changes, but so that he leaves.”
The demonstration comes after a whirlwind week that saw an uprising by a tiny military unit put down by government forces, fires set during protests in poor neighborhoods and the brief detention by security forces of Guaido.
Over the last two nights, Venezuelans angry over their country’s spiraling hyperinflation and food and medical shortages have gathered in the streets banging pots and pans and setting up barricades in protest. In the city of San Felix, residents set fire to a statue of Maduro’s mentor and predecessor, the late Hugo Chavez.
In the southern city of Ciudad Bolivar, a 30-year-old worker, Carlos Olivares, was killed when four unidentified men descended from a beige Jeep and fired upon a crowd that was looting a store. Two more unidentified people were also killed, according to a police report of the incident, and two were injured.
For much of the last two years, following a deadly crackdown on the 2017 protests and the failure of negotiations ahead of last May’s boycotted presidential election, the coalition of opposition parties has been badly divided over strategy and other differences as millions of desperate Venezuelans fled the country’s hyperinflation and widespread food shortages. But buoyed by unprecedented international criticism of Maduro, anti-government forces have put aside their infighting and are projecting a united front.
Guaido, who is taking the reins from a long list of better-known predecessors who have been exiled, outlawed or jailed, was dragged from an SUV just over a week ago by intelligence agents, but was quickly released amid an international outcry.
In the run-up to Wednesday’s protests, the defiant young lawmaker crisscrossed Caracas attending outdoor assemblies known as “Open Cabildos” — named for the revolutionary citizen councils held against Spanish colonial rule — pumping up crowds by arguing that Maduro must go for democracy to be restored.
“We are tired of this disaster,” he said Monday from the roof of a college building. “We know this isn’t a fight of a single day, but one that requires lots of resistance.”
An enthusiastic crowd of students answered with shouts of “Freedom!”
Driving the crisis was Maduro’s decision to ignore international opposition and take the presidential oath on Jan. 10 for a second term widely considered illegitimate after his main opponents were banned from running against him.
Guaido has been targeting his message to Venezuela’s military, the traditional arbiter of political disputes.
Maduro, who lacks the military pedigree of his mentor, Chavez, has sought to shore up support from the armed forces by giving key posts to top generals, including heading the PDVSA oil monopoly that is the source of virtually all of Venezuela’s export earnings. He has also been playing commander in chief, appearing last week at a military command meeting wearing camouflage fatigues and receiving the blessing of the defense minister, Gen. Vladimir Padrino Lopez.
But beyond the public displays of loyalty from the top brass, a number of cracks have started to appear.
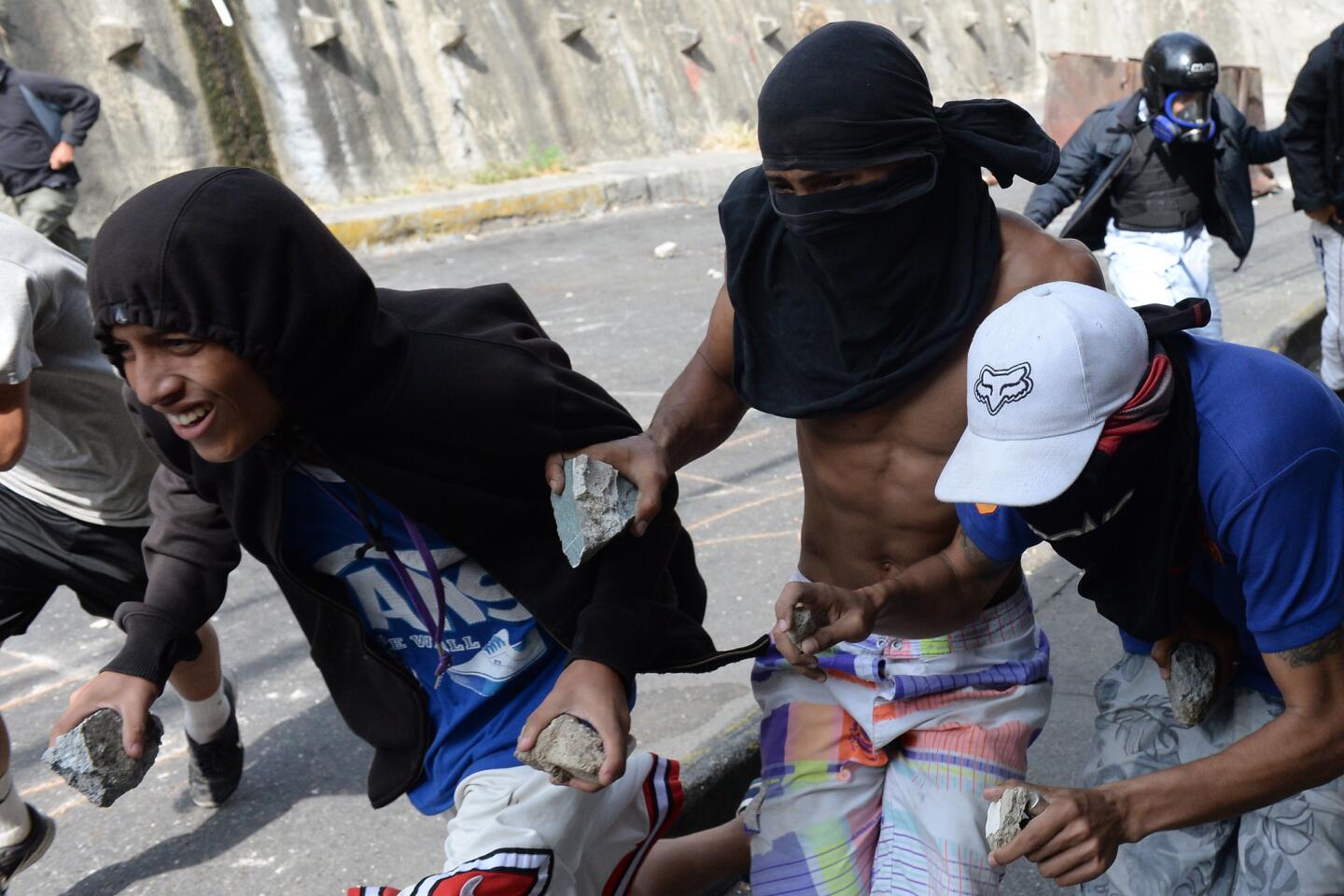
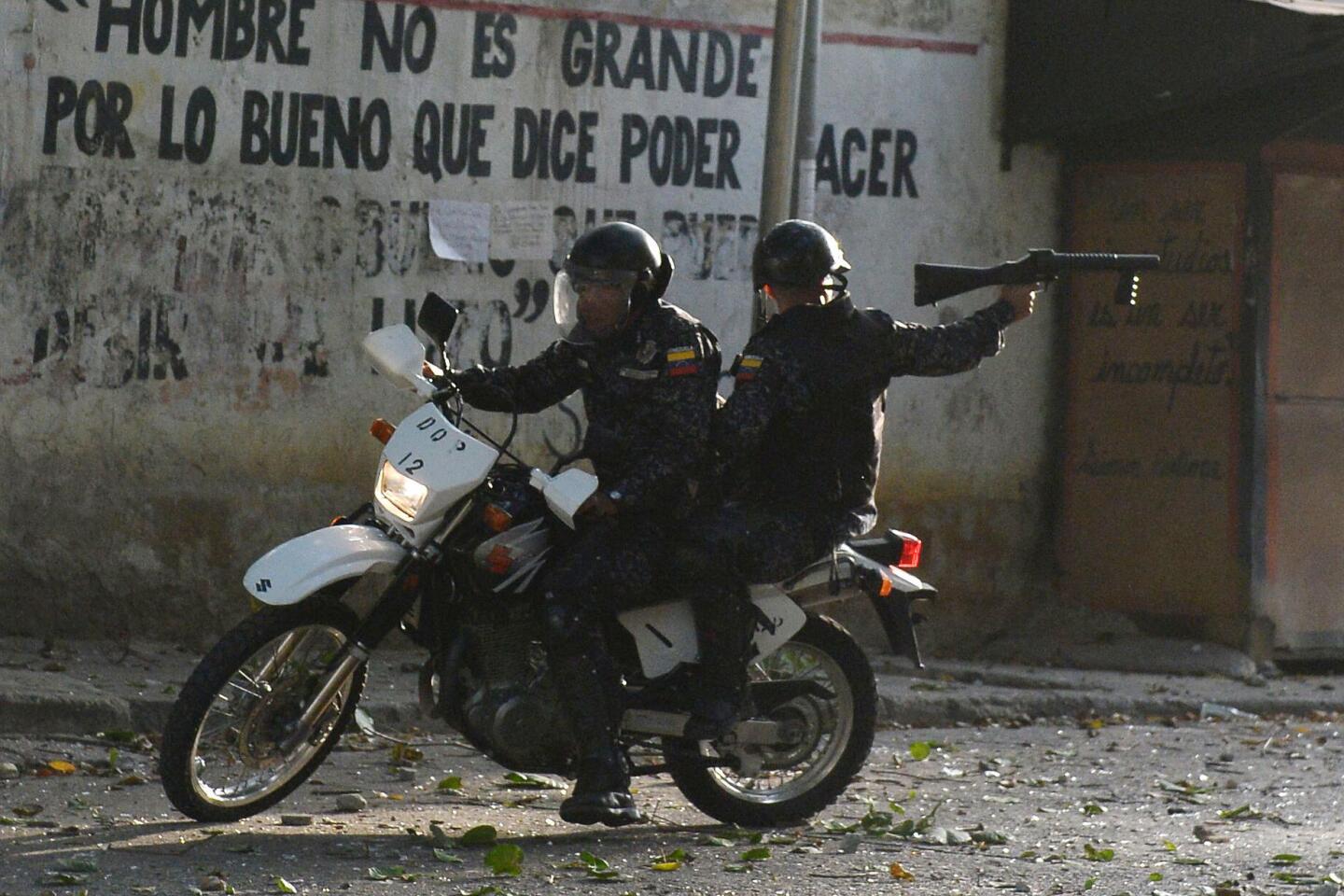
On Monday, Venezuelans awoke to news that a few dozen national guardsmen had taken captive a loyalist officer and seized a stockpile of assault rifles in a predawn raid. The government quickly quelled the uprising, but residents in a nearby slum took to the streets to show their support for the mutineers by burning cars and throwing stones at security forces, who fired back with tear gas.
Disturbances continued into Tuesday, with small pockets of unrest in a few working-class neighborhoods where the government has traditionally enjoyed strong support. More violence was reported Tuesday night.
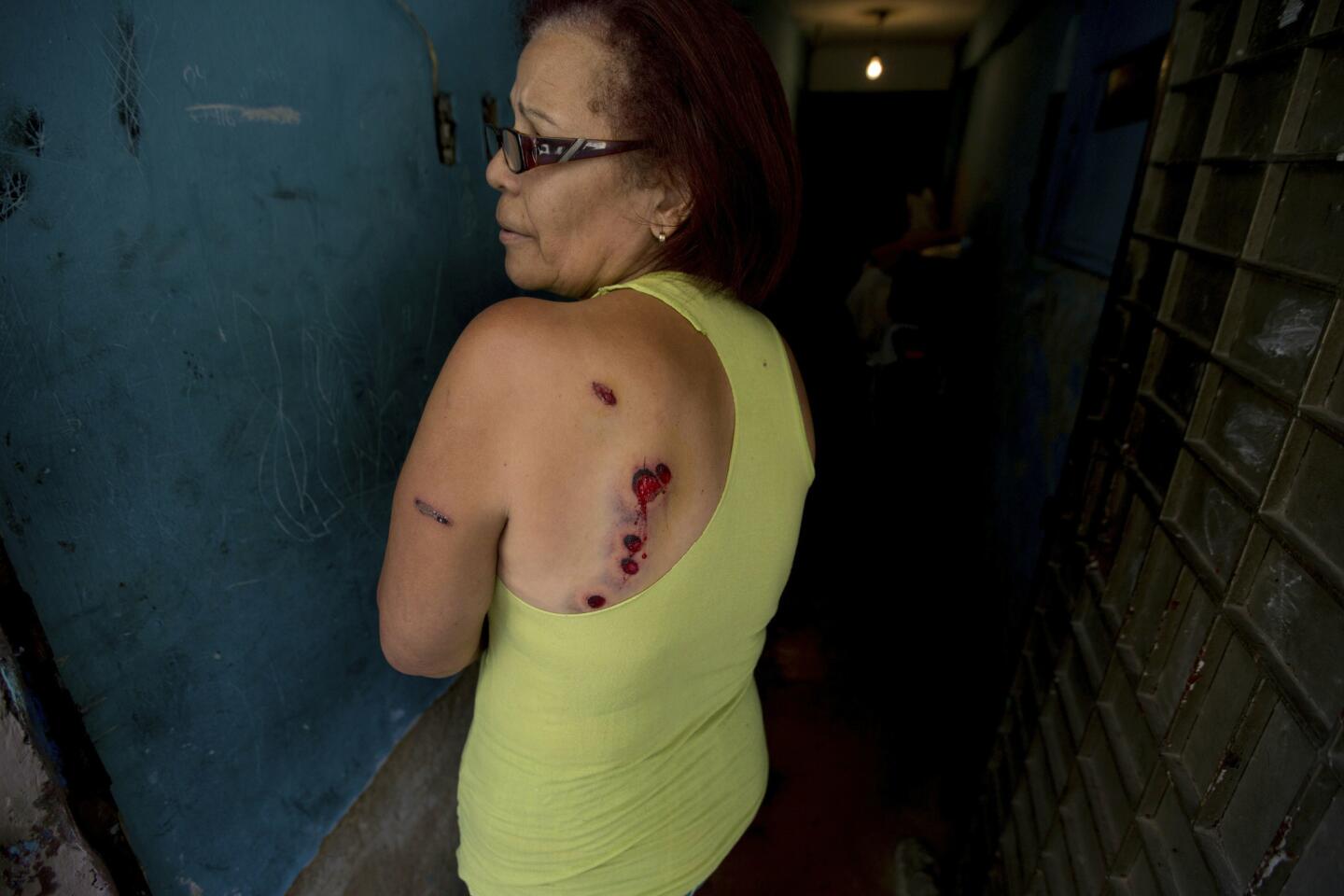
“People are tired of so much misery,” said Carmen Marcano, holding up her shirt to show seven buckshot wounds suffered during the clashes in the Cotiza slum next to where the rebellious guardsmen were captured.
Retired Maj. Gen. Cliver Alcala, a onetime aide to Chavez and now in exile, said the opposition’s newfound momentum has reverberated with the military’s lower ranks, many of whom are suffering the same hardships as regular Venezuelan families.
“I am absolutely certain that right now, especially younger troops are asking themselves whether Maduro is their commander in chief or a usurper,” Alcala said. “As we say in the barracks, hunger is the only thing that can devour fear of the government.”
Maduro has accused the opposition of inciting violence with the aim of provoking a bloodbath. Top socialist leaders have threatened to unleash on demonstrators menacing motorcycle gangs of pro-government die-hards known as colectivos.
“I demand the full rigor of the law against the fascists,” Maduro said Tuesday night, blaming what he called “terrorists” allegedly linked to Guaido’s Popular Will party for a fire at a cultural center named for a pro-government lawmaker slain in 2014.
He also accused U.S. Vice President Mike Pence of trying to foment unrest after Pence released a video pledging support, in Spanish, for the planned demonstrations.
Though intimidation has worked for the government in the past, it may not this time, said Dimitris Pantoulas, a Caracas-based political analyst. Discontent now appears to be more widespread and the ranks of security forces and government-allied groups have been thinned by the mass exodus of mostly young Venezuelans, he said.
“The government is resorting to its old tricks, but the people no longer believe them,” Pantoulas said.
More to Read
Start your day right
Sign up for Essential California for news, features and recommendations from the L.A. Times and beyond in your inbox six days a week.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.