An auto dealer keeps checking my credit. Is that a problem?

- Share via
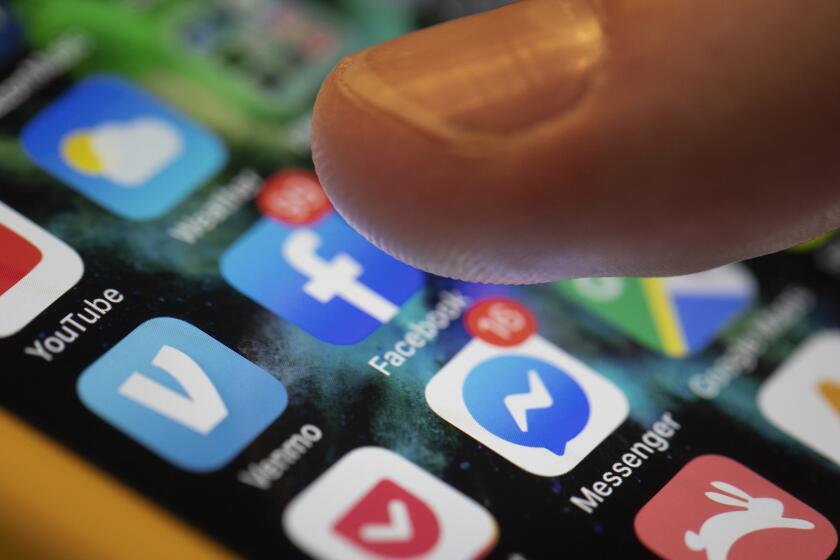
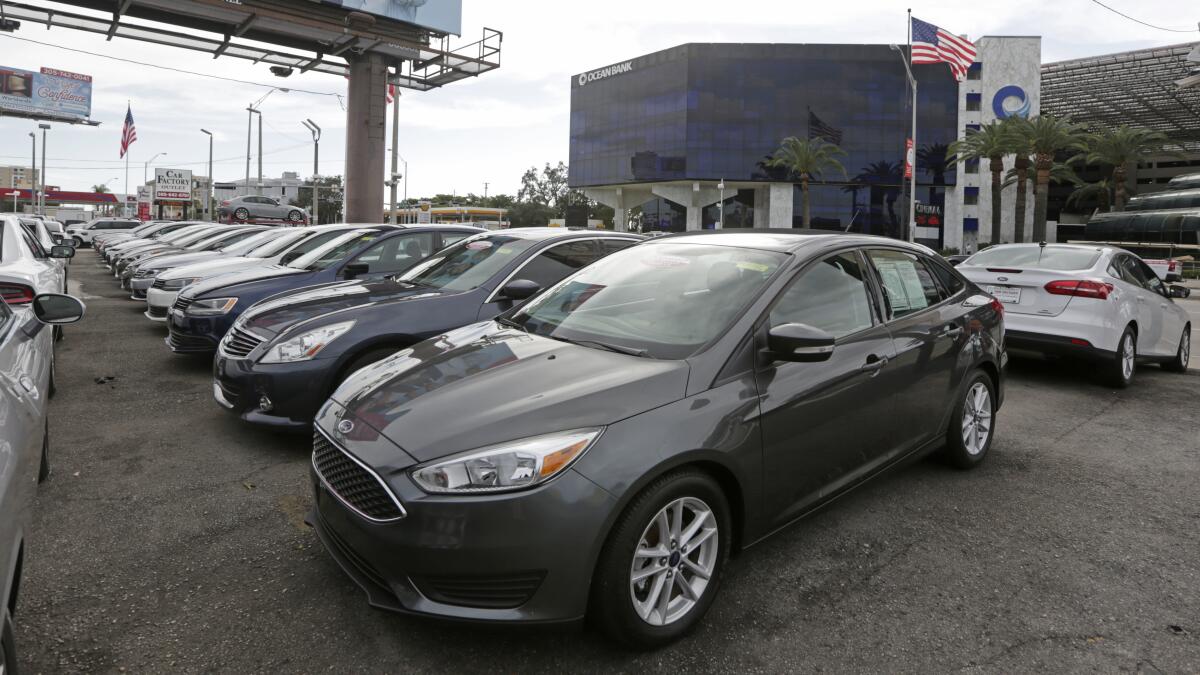
Dear Liz: How do I remove inquiries from multiple auto lenders? One of the dealerships pulled my credit at least eight times over a two-day period. I thought this could only be done while the customer is physically at the car lot.
Answer: Dealerships aren’t supposed to check your credit without your permission, and they can’t check your credit if you don’t give them your personal information, including your Social Security number. Some dealers use deceptive methods to get your personal information, such as claiming they need your Social Security number for you to take a test drive. (They don’t.)
If you did give permission, though, there’s not a lot you can do about multiple inquiries. Dealerships can, and will, check with multiple lenders to see what rates and terms they’ll offer you. If your credit isn’t great, multiple inquiries may be necessary to find you a loan.
The good news is that multiple auto loan inquiries in a two-day span won’t hurt your credit that much or for that long. Most credit scoring formulas don’t count each auto loan inquiry separately, but instead aggregate such inquiries together and count them as one. The ding against your credit scores is typically small and lasts only a few months.
Ideally, though, you wouldn’t continue to do business with a dealership that wasn’t crystal clear about why it needed your personal information and how it was going to be used. Also, consider applying for a car loan from a local credit union before you step onto a car lot. Credit unions are member-owned and tend to have good rates and terms, without the runarounds and add-ons that are so prevalent at car dealerships.
Rules enacted during the Trump administration have finally taken effect, giving debt collectors the ability to reach people via digital means.
DIY estate planning is unwise
Dear Liz: Please tell us about some estate planning tools that many might be able to use for themselves without incurring attorney fees and probate costs, such as naming payment-on-death beneficiaries at financial institutions and using real estate deeds with transfer-on-death provisions.
Answer: There are a number of ways that people can avoid probate, which is the court-supervised process of settling someone’s estate. Bank, financial and retirement accounts can pass to named beneficiaries outside probate, as can life insurance. Property owned in joint tenancy also avoids probate. Some states have transfer-on-death options for real estate and for vehicles.
The fact that you can avoid probate with these methods, however, doesn’t necessarily mean that you should.
Do-it-yourself estate planning can create a mess for your heirs that could incur far more in legal fees than you would have spent getting expert, personalized advice in the first place. A good rule of thumb: If you can afford to hire an estate planning attorney, you probably should.
Also, you shouldn’t automatically assume that probate is worth avoiding.
Probate is often lengthy and expensive in California and Florida, but may be far less cumbersome elsewhere. In addition, small estates typically qualify for simplified probate that’s faster and cheaper.
Probate also has some advantages, including limiting the time creditors have to make claims against your estate. You also might prefer a court’s supervision if you have contentious heirs or you’re concerned that your executor might not carry out your wishes.
These retirement researchers suggest maximizing Social Security and basing account withdrawals on the IRS’ required minimum distribution percentages.
How Social Security child benefits work
Dear Liz: I am drawing Social Security and my daughter just turned 18. Will she lose her Social Security and can I claim my wife in her place?
Answer: Child benefits, which is what your daughter receives, are designed to help the dependent minor children of Social Security recipients who are retired, disabled or deceased.
If your daughter is still a full-time high school student, then her child benefit can continue until she graduates or turns 19, whichever comes first. Otherwise the benefit typically ends at 18. (A child 18 and over with a disability can continue to get child benefits, as long as the disability started before age 22.)
Child benefits are only for the unmarried children of Social Security recipients, so obviously your wife doesn’t qualify. She may be eligible for her own Social Security benefit if she’s at least 62, or a spousal benefit based on your work record if that’s larger than her own benefit. AARP has a free Social Security claiming calculator that could help her sort through her options.
Liz Weston, Certified Financial Planner, is a personal finance columnist for NerdWallet. Questions may be sent to her at 3940 Laurel Canyon, No. 238, Studio City, CA 91604, or by using the “Contact” form at asklizweston.com.
More to Read
Inside the business of entertainment
The Wide Shot brings you news, analysis and insights on everything from streaming wars to production — and what it all means for the future.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.