Just off California, octopuses are converging by the thousands. Here’s why

- Share via
It was the last hour of a 30-hour dive, nearly two murky miles below the ocean’s surface.
A remotely operated vehicle called the Hercules was exploring the foothills of the Davidson Seamount, an underwater volcano 75 miles west of San Simeon.
Aboard the boat carrying the researchers who were monitoring the Hercules, it was expected to be a fairly boring dive, said Chad King, chief scientist on the 2018 cruise. Much research had been done near the top and slope of the seamount, but King and his fellow scientists wanted to explore around its base, expecting to find little sponges or corals amid lots of seafloor muck.
But then, just as Hercules crossed over a ridge, a curious sight floated across the screen: small, almost iridescent bulbs clinging to the seamount wall. The scientists directed Hercules down, farther into the depths.
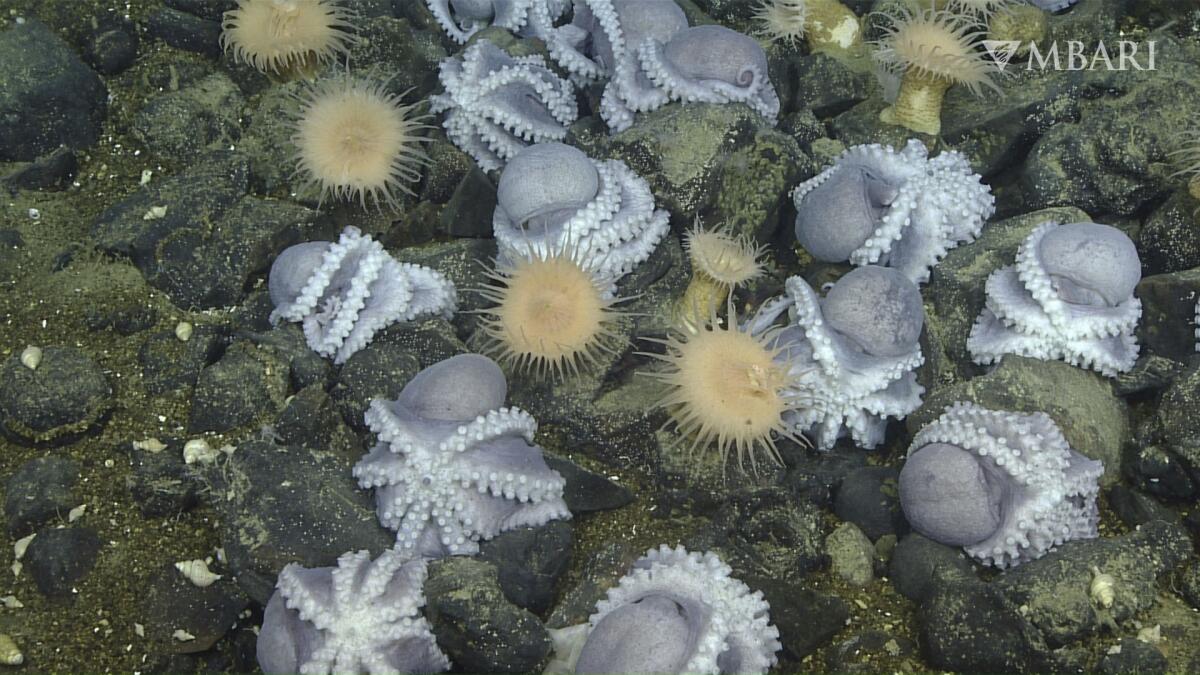
“And sure enough, that’s where we ran into thousands and thousands of these octopus,” King said. “And we were just absolutely floored. We were just giddy.”
The scientists, led by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary, had alighted upon what they called an “octopus garden.” The images they captured revealed nearly 6,000 octopuses — leading scientists to estimate the total population of the area could exceed 20,000.
The discovery of the thousands of Muusoctopus robustus — or “pearl octopus,” as researchers dubbed it for the animal’s shape and opalescent shine — led a team of scientists on a five-year quest to solve the mystery: Why are there so many thousands of pearl octopuses at the foot of the Davidson Seamount, and how did they come to be living there?
The researchers visited Octopus Garden more than a dozen times to find out, and a study published last week in the journal Science Advances shows they solved one part of the mystery. The pearl octopus came to the Davidson Seamount, they discovered, to nestle into the warm crooks of its wall and brood eggs.
The ambient temperature of water around the seamount is about 35 degrees Fahrenheit, according to Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute scientists. But by using sophisticated marine thermometers, the researchers found that the octopuses were settling into crevices warmed by spring water, where the temperature reached nearly 51 degrees.
“So we’re still unsure exactly about what kind of geological circulation drives these springs, but essentially water’s getting heated somewhere underground there,” said Steve Litvin, a marine ecologist at the institute. “And just like a warm spring, you know, I don’t want to say ‘Old Faithful,’ but it’s bubbling up there out of the rocks.”
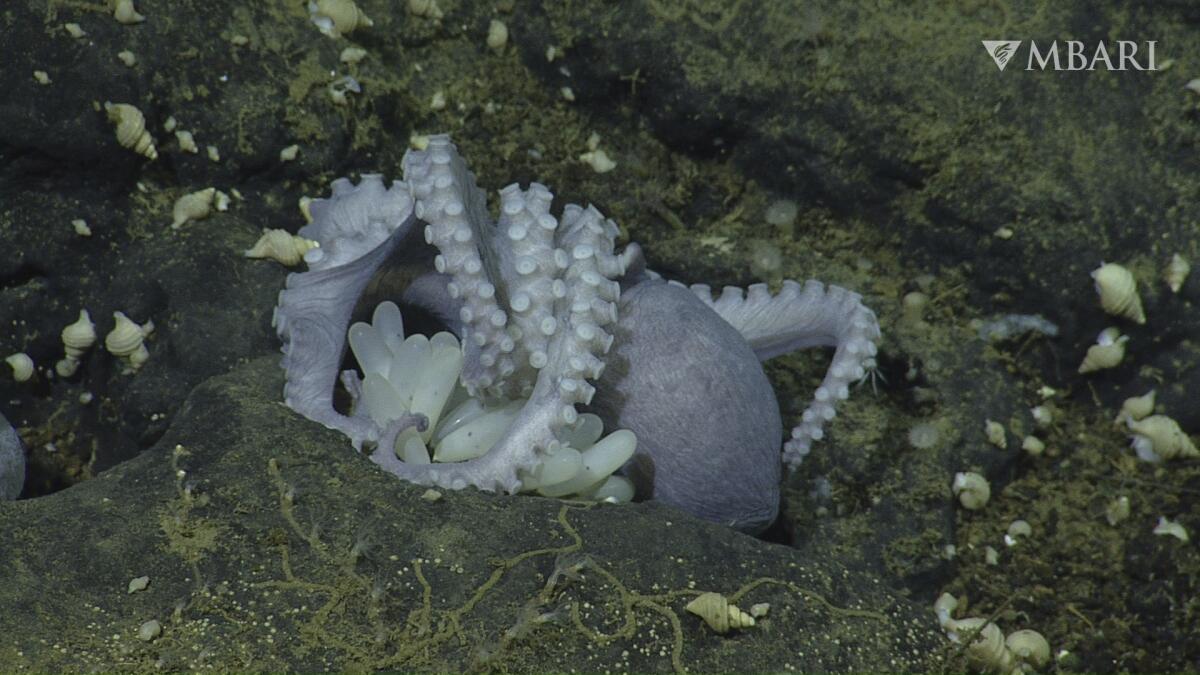

The relatively warm spring water raises the mother octopus’ metabolism, speeding up the egg development process. Researchers found that octopus eggs in the area hatch in less than two years — far less than the estimated five to eight years it takes in colder temperatures.
“They’re in warm water, the metabolism is much faster,” King said, “so their life history has been very compressed relative to most deep-sea animals.”
Solving one mystery only ignited a burst of other questions for the scientists: Where did the octopus come from? Does the animal instinctively know that the warm waters will speed up the brooding process? How many other octopus nurseries exist on the seafloor around the world?
“We know so little about the deep ocean,” Litvin said. “The discovery of the garden and all these thousands of octopus … just highlights that this is the biggest ecosystem on our planet, and we know less about it than we know about the surface of the moon.”
Lisa Levin, a deep-sea biologist who was not involved in the study, noted that other studies had found warmth around seamounts and shown that other animals live around underwater volcanoes. But she called this study’s discovery about how warm water affects octopuses’ brooding time “interesting, exciting and important.”
“I think the idea that warm fluids can speed up reproduction and that animals have evolved to use this is probably more widespread than we know, and we’re just beginning to discover how this happens and where,” said Levin, professor emerita at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego.
Just like the Beatles song “Octopus’s Garden,” she added, this nursery was found “in the shade” and “near a cave.”
“There’s something very prescient in there,” Levin said of the song. “It sounds a little bit like where they found these things.”
Scientists still don’t know where the grapefruit-sized octopuses came from, or how they knew to settle against the Davidson Seamount’s warm rocks. But over years of monitoring them, they watched the octopuses mate, settle, brood and hatch new offspring.
After the eggs hatch, the mother octopus dies. Shrimps, snails, anemones and other organisms feed off the octopus’ carcass. Most deep-sea animals rely on food floating down from the ocean surface — “marine snow,” Litvin called it. But with such a large number of octopuses living and dying in one area, he said, they provide the seafloor community “about 70% more carbon, more food than if only that marine snow was coming down.”
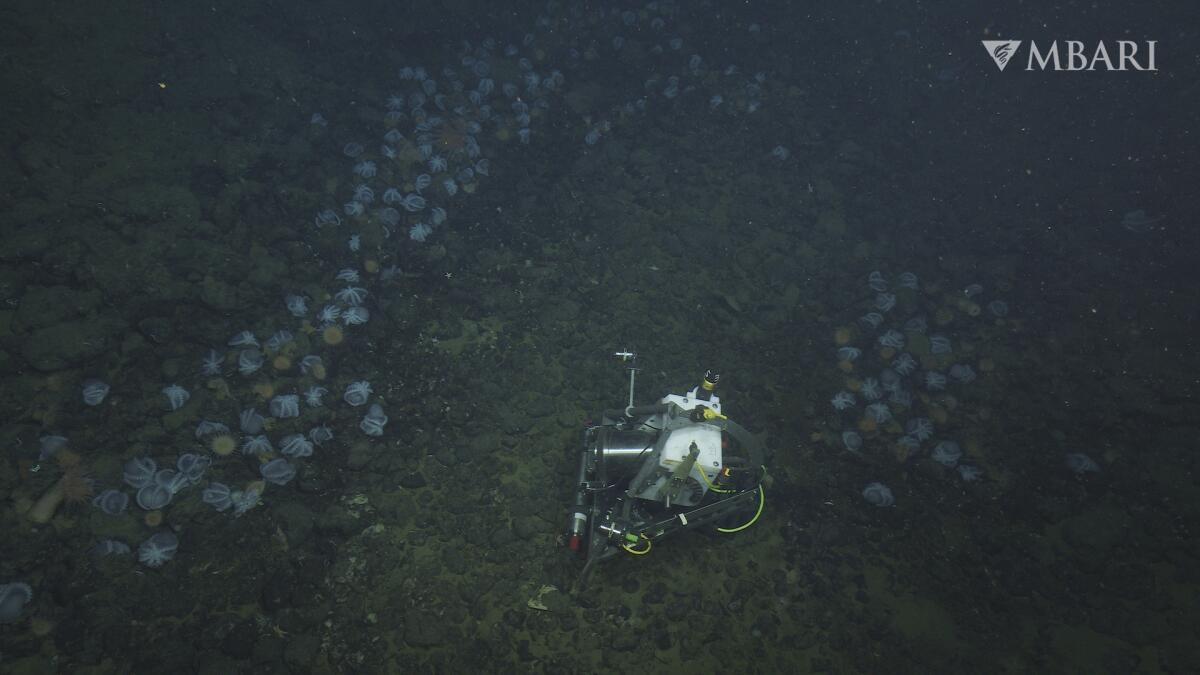

“You wouldn’t see this specific ecosystem at the garden,” Litvin said, “if it wasn’t for all those octopus dying.”
Once hatched, the juveniles swim off into the darkness, he said. Where do they go? That’s a question for future research to answer, he said.
“The thought that these kinds of ecosystems are still hiding from us — that after a couple of decades of a lot of deep-sea exploration, there’s still that scale of a discovery — is just amazing,” Litvin said, “and really highlights the need for continued investment in technology so we can expand our efforts to explore the deep sea, find the next Octopus Garden and literally, again, understand how that biggest ecosystem in our planet works.”
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.