Must Reads: In Central Valley towns, California’s bullet train isn’t an idea: ‘It’s people’s lives’

- Share via
Reporting from Fairmead, Calif. — When Annie Williams heard that California’s plan for high-speed rail had been scaled back to 119 miles through the Central Valley, her head jerked back.
“Merced to Bakersfield? The good Lord himself can’t make sense of that,” she said. “After all our tears and making peace?”
The recent debate surrounding California’s transit future has reverberated statewide. But here in the Central Valley, the upheaval — like the bullet train itself — is real. Houses have been boarded up, businesses moved, vineyards torn out, a highway realigned.
Giant concrete structures rise from orchards waiting to hold up tracks that now seem further from existence.
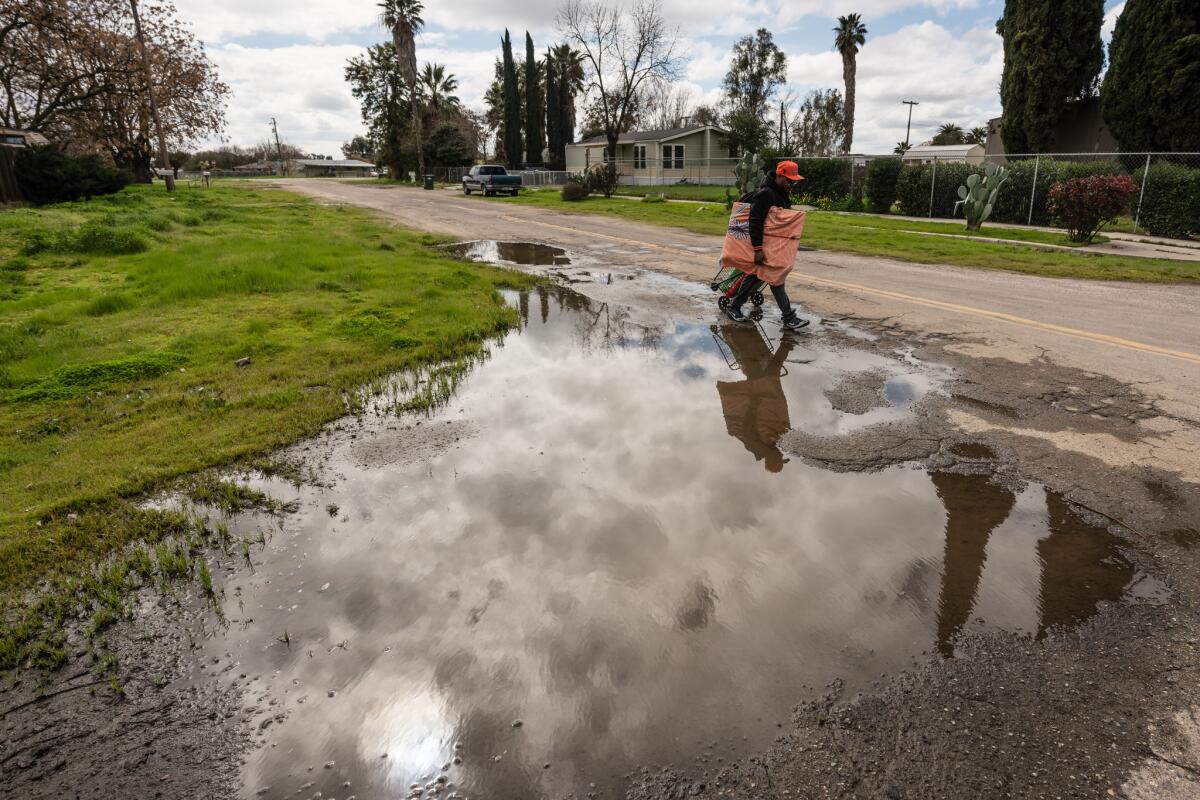
Fairmead, the community where Williams lives, is the likely place that will face the most immediate uncertainties. It is in the “Y,” the planned fork from which some trains were to hurtle south toward Los Angeles or north to Merced, and others were to veer west to the Bay Area.
There is no library or market or gas station here; only three buildings in the town of about 1,500, including the church, aren’t people’s homes. Sheds lean, grass grows through porch slats and rains leave deep puddles on dirt and gravel roads.
Williams, who gives her age as “upwards of 70,” said this is a place where people “work hard to have a place just to lay their heads and have been taking care of each other since nigh the beginning of time.”
An early proposed high-speed rail would have leveled a neighborhood, including Williams’ home. But that was before community organizers Vickie Ortiz and Barbara Nelson rallied their neighbors.
Their nonprofit organization, Friends of Fairmead, held so many meetings to lobby state representatives for a different route that the women started greeting the rail agency’s regional director with familiar hugs. After nearly a decade of negotiating, they felt they were a breath away from a route that would move the school, spare the church, preserve more houses and bring the town a much-needed community center.
Then in mid-January, Gov. Gavin Newsom laid out plans to pull back on high-speed rail in the face of massive cost overruns.
“I think the community center is gone,” the lawyer for Friends of Fairmead said.
Ortiz is angry about all the years she watched people worry and fret about where they would go.
“I don’t want to talk political because I don’t do it very well,” Ortiz said. “But you know, you had a governor that was pushing-pushing-pushing for the high-speed train, and we started getting used to the idea that we can’t stop a train but maybe we can use it to help the community. But then you get another governor and he says: ‘No, I don’t want to do that anymore.’ My mouth was just open with shock.”
Nelson, however, said she felt relief.
Each week, she visits an elderly neighbor in the hospital who asks her the latest about whether the project will take her house.
“I’m going to tell her, ‘Sister Hughes, your house is safe.’ And we’ll find some other way to get our community center.”
Traveling south from Fairmead on California Route 99, there’s a stretch of highway through Fresno that’s smooth and new. Five bridges were torn down and rebuilt in order to move the road about 100 feet to make room for rail. The California Department of Transportation project cost about $290 million.
Along the Kings River, near the little town of Laton, the signs of coming bullet train infrastructure include felled orchards and giant earthen berms. (Local independent truck drivers got weeks of work hauling dirt for the project.)
Next to the Van Eyk family’s walnut grove, where crops once grew, is now a stretch of excavated earth marked by “No Trespassing” signs.
Randy Van Eyk was born and raised on a dairy farm outside of nearby Hanford. His wife, Anne, grew up in rural Northern California. They lived in the city of Visalia for 10 years, saving for a place like this — a big house on a country road where they live with their 7-year old daughter, Maddie, a Labrador retriever named Snickers and a giant cat.
Randy planted walnuts instead of more lucrative almonds, because he was 45 years old when they moved in and almonds need replanting every 20 years. He didn’t want to work that hard at 65. Walnut trees should outlive him.
“We figured this was our last stop unless Maddie put us in a home someday,” Anne said.
The first sign that high-speed rail might change that was a giant white X painted on the road near their mailbox.
They found other Xs at other intersections and drew a diagonal line that went through their frontyard .
Anne cried — and, she said, she never cries.
Her husband told her not to worry, that it would never really happen. But work crews arrived, neighbors moved and cranes dropped off giant pipes. In the end, they were the only residents on their road that didn’t have to sell property to the state.
“We’ll have people over, even from around here, and they’ll look around and say: “That’s from high-speed rail? You mean it’s real?’ People think it’s just some idea, something to fight about on the radio, but it’s people’s lives,” Randy said.
The argument for a high-speed train crossing the state was that it would bridge California’s inequalities.
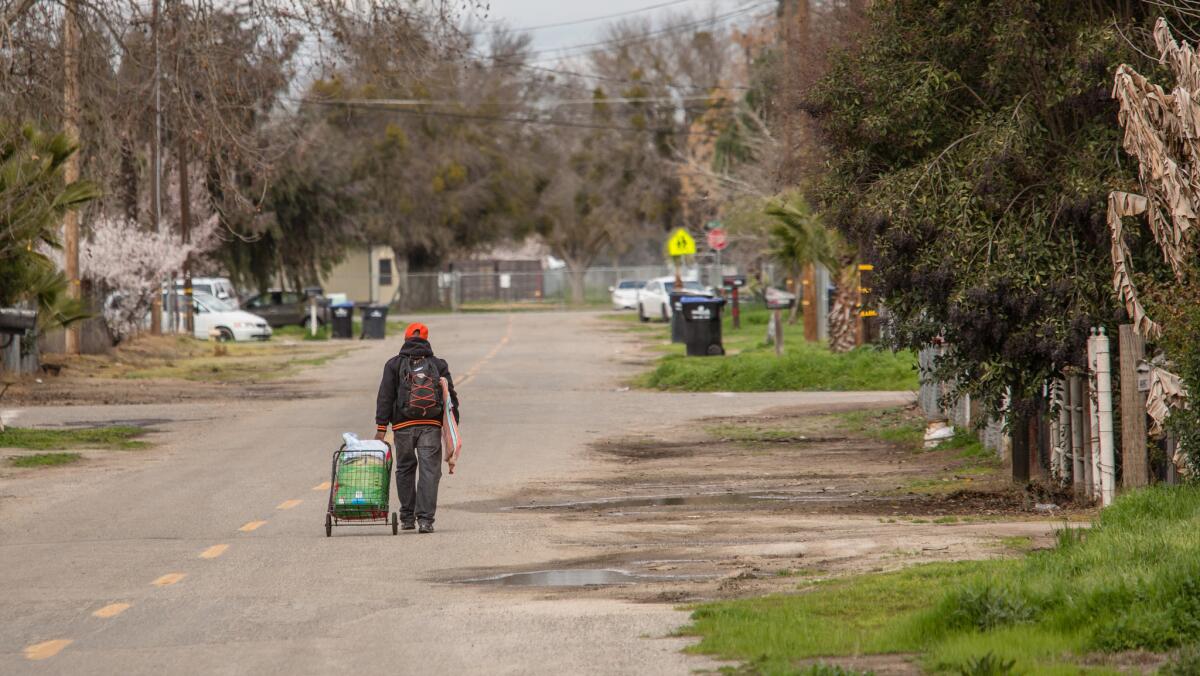
Central Valley cities and towns have some of the most concentrated poverty in the state. The political vision was that it would connect them to the wealth and opportunities of the coast and bring higher paying jobs. It would cut down on the air pollution that gets trapped in the hot, flat valley.
Randy Van Eyk was opposed to the project because he thought it would bring wealthy tech workers who would displace farms and rural life. He also thought politicians would start the project and never finish, leaving the debris in the Central Valley.
“You see all the destruction?” he said. “People lost their homes and businesses. And for what?”
He said he has flashes of anger, but then looks around and takes a deep breath.
“I look at the almond trees across the street and the bee boxes and that neighborhood dog coming over to play and think, ‘Yeah, it’s OK.’ That train is only going to Bakersfield. It’s not going to change anything.”
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.











