India authorizes COVID-19 vaccines from AstraZeneca and a domestic drugmaker

- Share via
NEW DELHI — India authorized two COVID-19 vaccines Sunday, paving the way for a huge inoculation program to stem the pandemic in the world’s second-most-populous country.
The country’s drugs regulator gave emergency authorization for the vaccine developed by Oxford University and U.K.-based drugmaker AstraZeneca, as well as another developed by Indian company Bharat Biotech.
Drugs Controller General Dr. Venugopal G. Somani said both vaccines would be administered in two doses. He said the decision to approve the vaccines was made after “careful examination” by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization, India’s pharmaceutical regulator.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi called the vaccine approval a “decisive turning point to strengthen a spirited fight.”
“It would make every Indian proud that the two vaccines that have been given emergency use approval are made in India!” Modi tweeted.
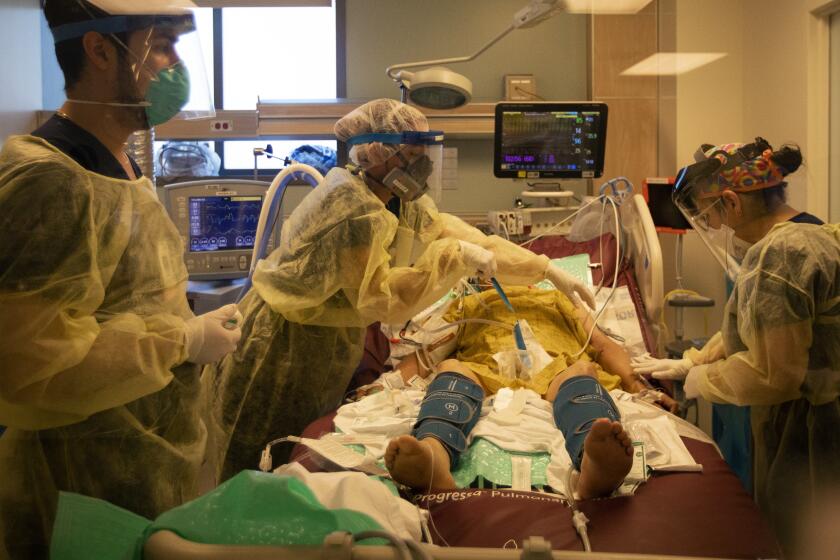
Los Angeles County posted its third highest single-day total for coronavirus cases on New Year’s Day
AstraZeneca has contracted Serum Institute of India, the world’s largest vaccine manufacturer, to make 1 billion doses of its vaccine for developing nations, including India. On Wednesday, Britain became the first country to approve the shot.
India, however, will not allow the export of the Oxford University-AstraZeneca vaccine for several months, Adar Poonawalla, Serum Institute’s CEO, said Sunday. The ban on exports means that poorer nations will probably have to wait a few months before receiving their first shots.
The move was made to ensure that vulnerable populations in India were protected and to prevent hoarding, Poonawalla told the AP.
But questions have been raised by health experts over the vaccine developed by Bharat Biotech. They point out that clinical trials have begun only recently, making it almost impossible for the firm to have analyzed and submitted data showing that its shots are effective in preventing illness from the coronavirus.
India has confirmed more than 10.3 million cases of the virus, second in the world behind the U.S., though its rate of infection has come down significantly from a mid-September peak. It also has reported over 149,000 deaths.
The country’s initial immunization plan aims to vaccinate by August 300 million people — healthcare workers, frontline staff including police, and those considered vulnerable due to their age or disease. For effective distribution, more than 20,000 health workers have been trained so far to administer the vaccine, the Health Ministry said.
But the plan poses a major challenge. India has one of the world’s largest immunization programs, but it isn’t geared around adults, and vaccine coverage remains patchy. Still, neither of the approved vaccines requires the ultra-cold storage facilities that some others do. Instead they can be stored in refrigerators, making them more feasible for the country.
Although Serum Institute of India doesn’t have a written agreement with the Indian government, Poonawalla said India would be “given priority” and would receive most of its stockpile of around 50 million doses.
Partial results from studies for the Oxford-AstraZeneca shot in almost 24,000 people in Britain, Brazil and South Africa suggest that the vaccine is safe and about 70% effective. That isn’t as good as some other vaccine candidates, and there are also concerns about how well the vaccine will protect older people.
The other vaccine authorized by India, known as Covaxin, is developed by Bharat Biotech in collaboration with government agencies and is based on an inactivated form of the coronavirus. Early clinical studies showed that the vaccine didn’t have any serious side effects and produced antibodies for COVID-19. But late clinical trials began in mid-November. The second shot was to be given 28 days after the first, and an immune response prompted two weeks later.
That time frame means that it isn’t possible that the company has submitted data showing that the shots are effective in preventing infection from the virus, said Dr. Gagandeep Kang, an infectious diseases expert at the Christian Medical College at Vellore.
All India Drug Action Network, a public health watchdog, issued a statement demanding greater transparency.
Somani, the regulator, says “the vaccine has been found to be safe” but has refused to say whether any efficacy data have been shared.
The Health Ministry said in a statement that permission was granted for Bharat Biotech’s shot for restricted use in the “public interest as an abundant precaution in clinical trial mode, especially in the context of infection by mutant strains.”
But Kang said that the claim that the vaccine could help against a mutant variant of the virus was “hypothetical” and without any evidence.
Indian regulators are still considering approvals for other vaccines, including one made by Pfizer.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.